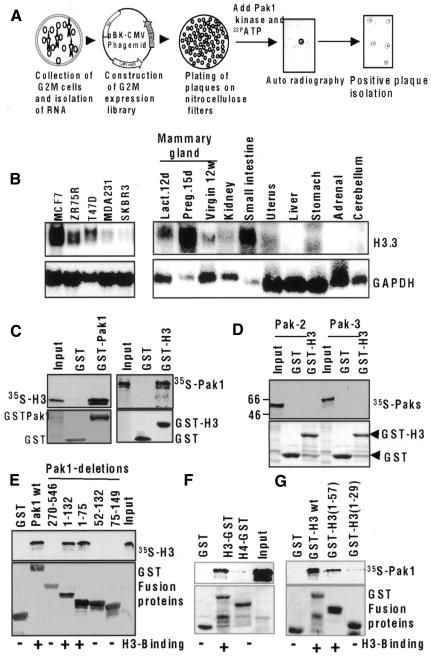
Fig. 2. Identification of histone H3.3A as a Pak1 substrate. (A) G2–M expression library screening by Pak1. (B) mRNA expression of H3.3A in breast cancer cell lines and murine tissues. (C) Direct interaction of Pak1 with histone H3 in a GST pull-down assay. In vitro-translated H3 bound to GST–Pak1 (left panel), and in vitro-translated Pak1 bound to GST–H3 (right panel). (D) Non-interaction of H3 with Pak 2 and Pak3. cDNAs were translated in vitro, incubated with GST–H3 and analyzed by a GST pull-down assay. (E) Interaction of Pak1 domains with histone H3. Pak1 GST-fusion proteins containing full-length Pak1 amino acids (aa 1–546), the kinase domain (aa 270–546), the N-terminal domain (aa 1–132), the Nck-binding domain (aa 1–75), the Cdc42/Rac-interacting domain (aa 52–132) and the autoinhibitory domain (aa 75–149) were all incubated with in vitro-translated H3, and binding was analyzed by a GST pull-down assay. (F) Pak1 specifically interacts with H3 but not H4 in TNT pull-down assays. GST pull-down assay using 35S-labeled Pak1 and GST fusion of H3 or H4. (G) Pak1 interacts with H3 tail. GST pull-down assay using 35S-labeled Pak1 and GST fusions of H3 1–57 or H3 1–29.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.