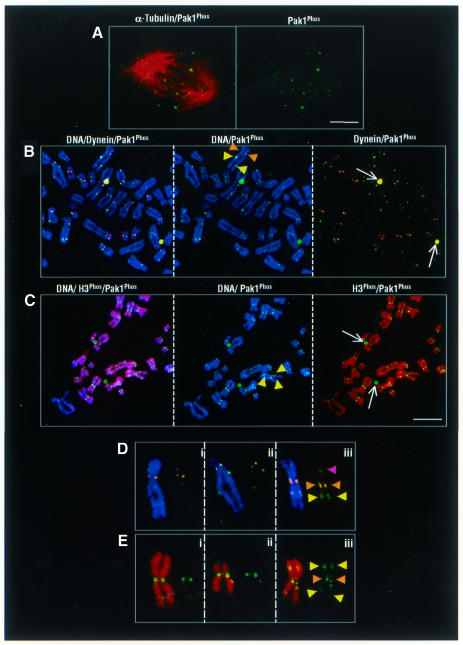
Fig. 4. Chromosomal localization of activated Pak1. (A) Metaphase plate localization of Pak1. Confocal micrographs of a single tangentially cut plane through a metaphase cell. Pak1Phos alone (right panel) and merged image with α-tubulin (left panel). (B) Centromeric and extracentromeric patterns of chromosome-bound activated Pak1, as revealed by three-color confocal microscopy of chromosome spreads obtained from colcemid-treated MDA-MB231 cells. Centromeric colocalization of dynein (red) and activated Pak1 (green) (brown arrowheads); extracentromeric localization of Pak1Phos (yellow arrowsheads). Dynein and Pak1 colocalization on centrosomes (white arrows) and in the centromeric region (brown arrowheads). (C) Centromeric and extracentromeric localization of activated Pak1 on chromosome spreads from MDA-MB231 cells. Activated Pak1 associated with condensed chromosomes containing histone H3 Ser10Phos. Histone H3 Ser10Phos (red), activated Pak1 (green); Topro-3 DNA staining (blue). Representative spreads are shown in merged colors in the left panel and in two colors in the middle and right panels. Note the activated Pak1 on both the centrosomes and chromosomes (white arrows and yellow arrowheads, respectively). Scale bar = 4 µm. (D) Extracentromeric localization of activated Pak1 immunoreactivity without dynein labeling (yellow arrowheads); Pak1 and dynein colocalization in the centromeric region (brown arrowheads). Unilateral Pak1 localization on the chromosome arm (purple arrowhead). (E) Representative examples of individual chromosomes in which activated Pak1 colocalized with histone H3 Ser10Phos in the extracentromeric (yellow arrowheads) regions.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.