Figure 2:
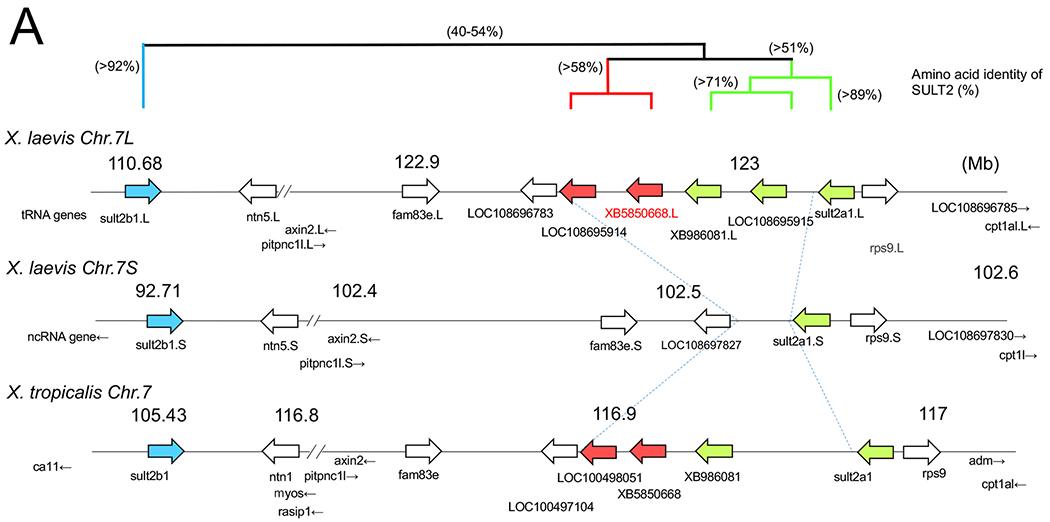
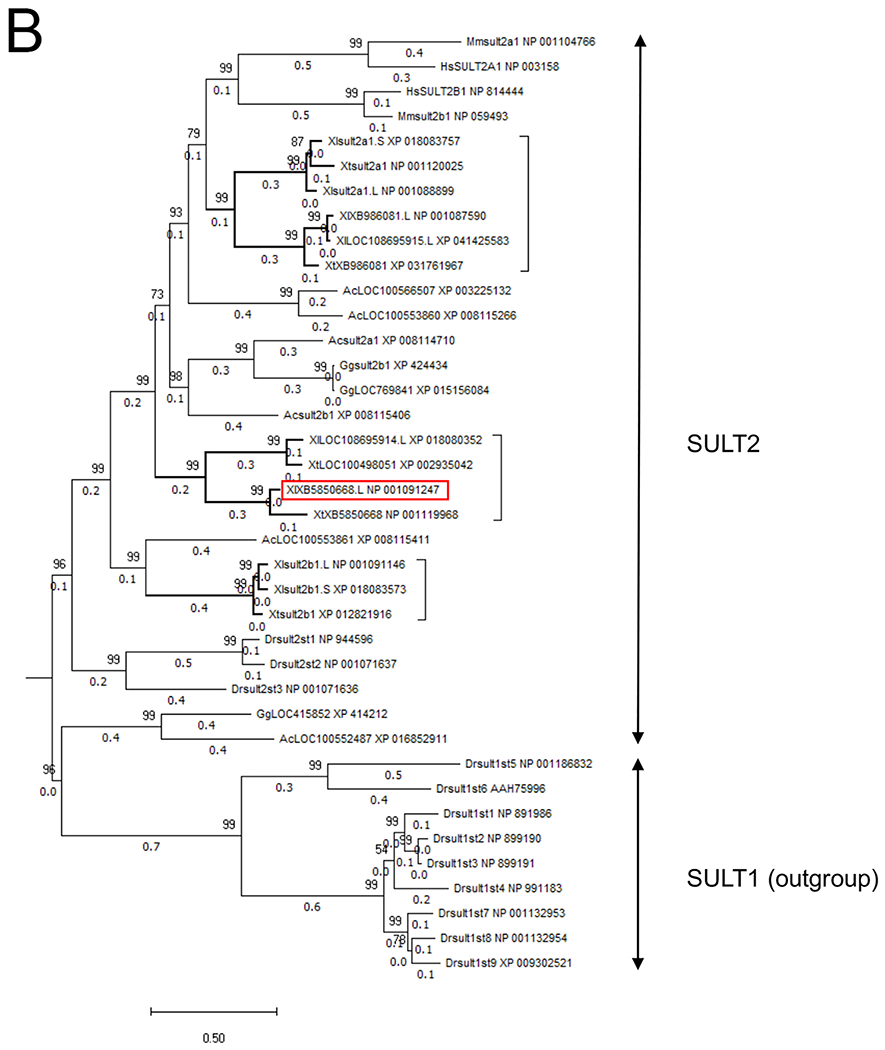
Chromosomal localization of the members of SULT2 gene family including XB5850668.L in Xenopus laevis and Xenopus tropicalis, and their phylogenetic relationships.
A: The loci of SULT2 family genes on Xenopus chromosome 7. The gene cluster consists of 6 members on the L-subgenome and 2 members on the S-subgenome in the allotetraploid X. laevis, and 5 members in the diploid X. tropicalis. Four members were lost from the S-subgenome in X. laevis. This chromosomal region showed shared synteny between X. laevis and X. tropicalis (see also Table 1), but little synteny across species from mammals to a teleost (see also Table 2). The three groups in the Xenopus SULT2 gene family are shown by bold arrows in blue, red, and green, and their phylogenetic relationships are depicted with amino acid identity (%) above the chromosomal maps.
B: Phylogenetic tree of the vertebrate SULT2 gene family. The tree was constructed with the maximum likelihood method from eight X. laevis (Xl), five X. tropicalis (Xt) and 16 other vertebrate SULT2 amino acid sequences and with nine Danio rerio (Dr) SULT1 amino acid sequences as an outgroup. Node values represent the Chi-square-based parametric values returned by the approximate likelihood ratio test. Gene and protein IDs, and annotations and other information for each member are shown in Table 1. The first two letters of the gene names denote the species: Ac, Anolis carolinensis (green anole); Dr, Danio rerio (zebrafish); Gg, Gallus gallus (chicken); Hs, Homo sapiens (human); Mm, Mus musculus (house mouse); Xl, Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog); and Xt, Xenopus tropicalis (western clawed frog). The last letter (S or L) of the gene names for Xenopus laevis indicate homeologs derived from either the S- or L-subgenome. The three groups in the Xenopus SULT2 gene family are shown by bold branches and a bracket, and the XB5850668.L gene is outlined by a red rectangle.
