Figure 5:
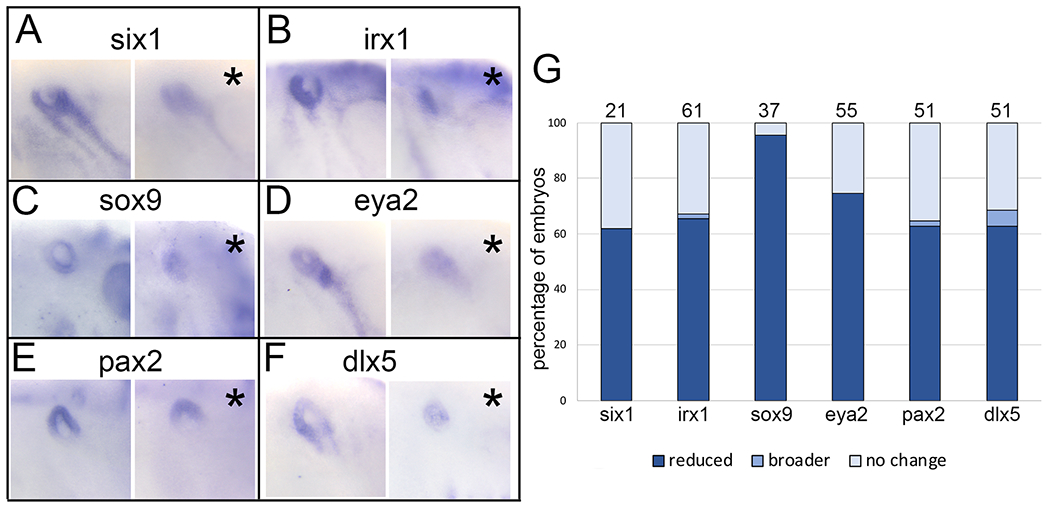
XB5850668.L is required for otic vesicle gene expression
A: Knockdown of XB5850668.L translation on one side of the larva (asterisk, right panel) results in reduced expression of six1 in the otic vesicle (OV, blue circle) compared to the control side of the same embryo (left panel).
B: Knockdown of XB5850668.L translation on one side of the larva (asterisk, right panel) results in reduced expression of irx1 in the OV (blue circle) compared to the control side of the same embryo (left panel).
C: Knockdown of XB5850668.L translation on one side of the larva (asterisk, right panel) results in reduced expression of sox9 in the OV (blue circle) compared to the control side of the same embryo (left panel).
D: Knockdown of XB5850668.L translation on one side of the larva (asterisk, right panel) results in reduced expression of eya2 in the OV (blue circle) compared to the control side of the same embryo (left panel).
E: Knockdown of XB5850668.L translation on one side of the larva (asterisk, right panel) results in reduced expression of pax2 in the OV (blue circle) compared to the control side of the same embryo (left panel).
F: Knockdown of XB5850668.L translation on one side of the larva (asterisk, right panel) results in reduced expression of dlx5 in the OV (blue circle) compared to the control side of the same embryo (left panel).
G: Percentage of embryos in which OV expression domains of genes were reduced (dark blue), broader (medium blue) or did not change (light blue) when analyzed at larval stages (st 28-32). The number of embryos analyzed for each gene is on top of each bar.
