Figure 8:
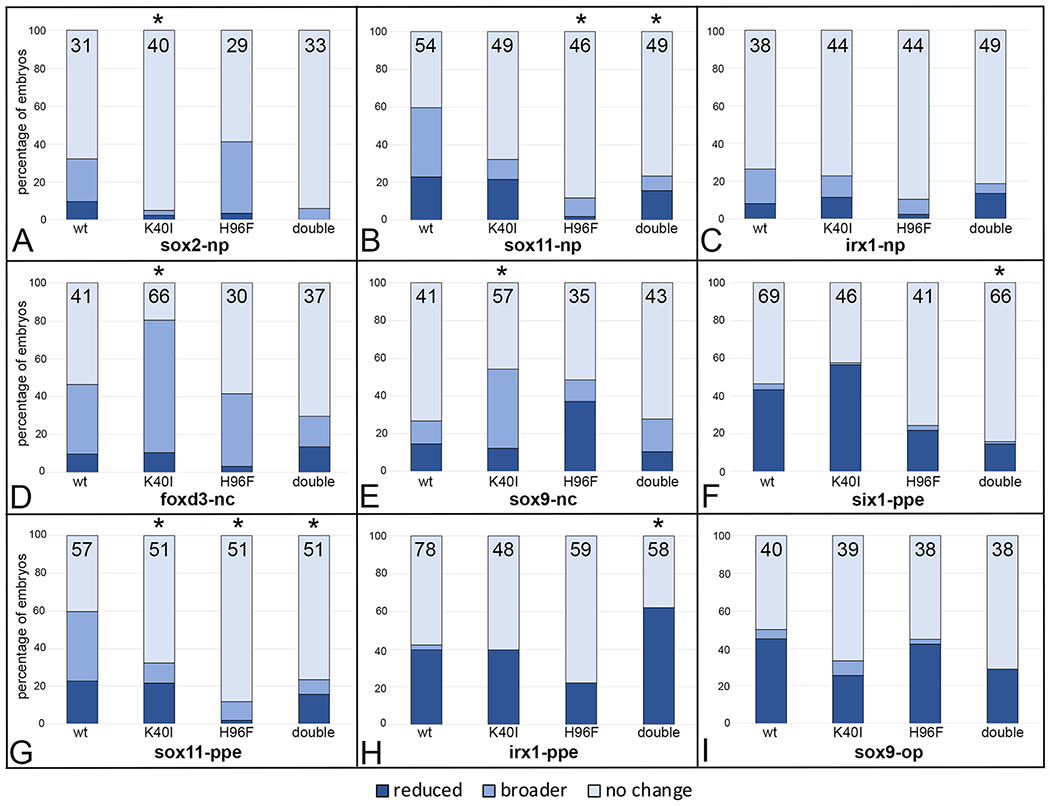
Mutation of amino acids in the PAPS binding (H40I) or catalytic (H96F) domains tend to attenuate effects of wild type XB5850668.L gain-of-function on ectodermal gene expression domains. The percentage of embryos in which the expression domain was reduced (dark blue), broader (medium blue) or did not change (light blue) after injections of mRNAs (100pg) encoding wild type (wt) or mutated versions (K40I, H96F, double = K40I+H96F) of XB5850668.L. The number of embryos analyzed is inside each bar. * indicates mutant mRNA phenotype frequencies that were significantly different from wt at the p<0.05 level (Chi square test).
A: sox2 neural plate (np) expression domain changes.
B: sox11 neural plate (np) expression domain changes.
C: irx1 neural plate (np) expression domain changes.
D: foxd3 neural crest (nc) expression domain changes.
E: sox9 neural crest (nc) expression domain changes.
F: six1 preplacodal (ppe) expression domain changes.
G: sox11 preplacodal (ppe) expression domain changes.
H: irx1 preplacodal (ppe) expression domain changes.
I: sox9 otic placode (op) expression domain changes.
