Figure1.
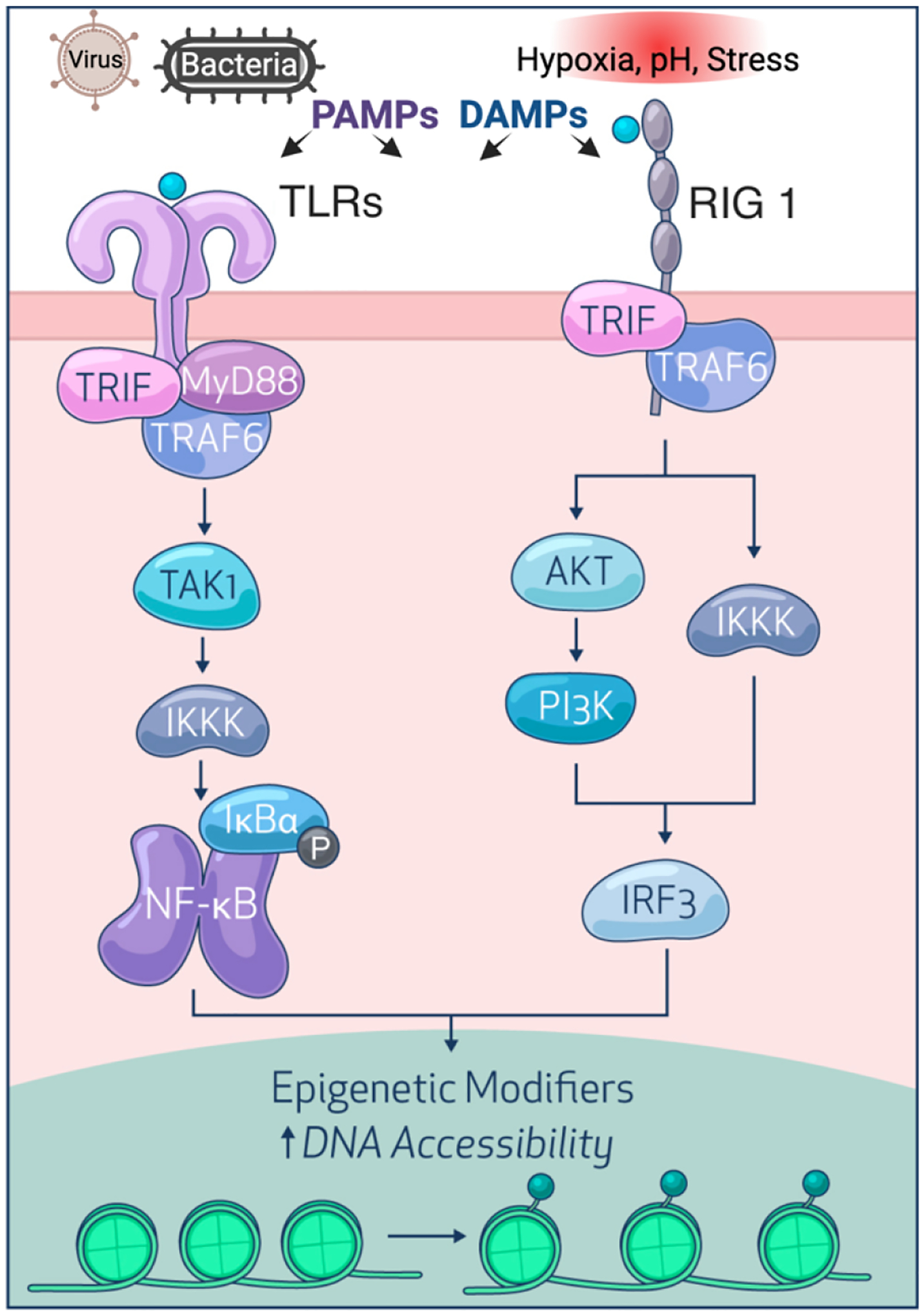
Transflammation. Viruses and bacteria produce PAMPs while hypoxia, pH, stress, and other injurious stimuli generate DAMPs, both of which trigger innate immune signaling by intracellular or transmembrane PRCs such as TLRs and RIG-I. Subsequently, NF-kB or IRF3 are activated and translocated to the nucleus to alter the expression of epigenetic modifiers, thereby increasing DNA accessibility to facilitate the cell fate transition.
