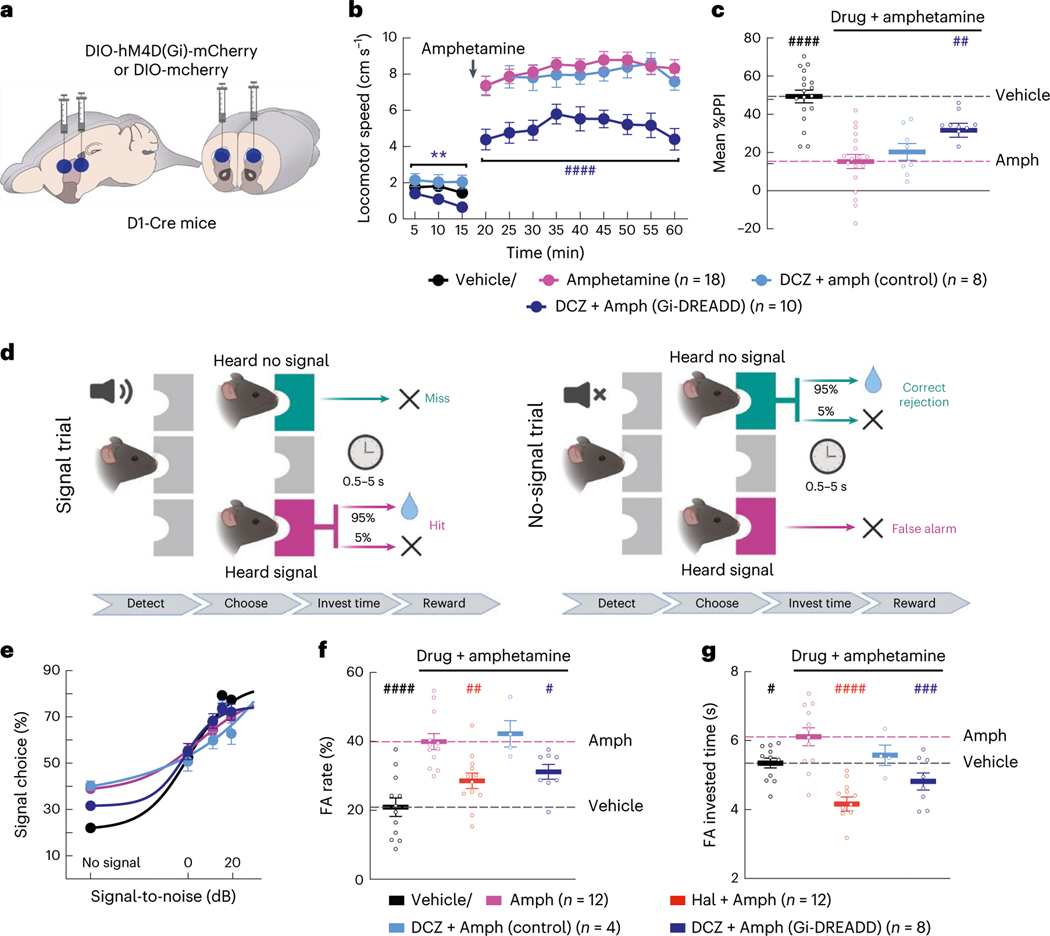
Fig. 4 |. Inhibiting D1-SPNs is sufficient to rescue amphetamine-driven behaviors.
a, We injected DIO-hM4D(Gi)-mCherry or DIO-mCherry virus bilaterally at two sites in the DMS of D1-Cre mice. b,c, Treatment with the DREADD agonist DCZ reduced baseline locomotion and attenuated amphetamine-driven hyperlocomotion (b) and PPI disruption (c) in DREADD, but not mCherry-expressing, mice (**P < 10−2 for comparison to vehicle-only treatment; ####P < 10−4 and ##P < 10−2 compared to vehicle + amphetamine treatment; two-way ANOVA (b) and one-way ANOVA (c) with Holm–Sidak’s multiple comparison test). d, Schematic of hallucination-like perception assay in which mice initiate trials by nose poking in the center port and choosing the left or right reward port depending on whether a tone is or is not embedded in the background white noise (created with BioRender). e–g, Psychometric function of the percentage of ‘heard signal’ choice (e), false alarm (FA) rate (f) and FA investment times (g) after vehicle or amphetamine treatment with or without haloperidol or DCZ pre-treatment. Data in e are mean ± 1 s.d. binomial confidence intervals and mean ± s.e.m. in f and g (####P < 10−4, ###P < 10−3, ##P < 10−2 and #P < 0.05 compared to vehicle + amphetamine treatment; one-way ANOVA with Holm–Sidak’s multiple comparison test).