Figure 1.
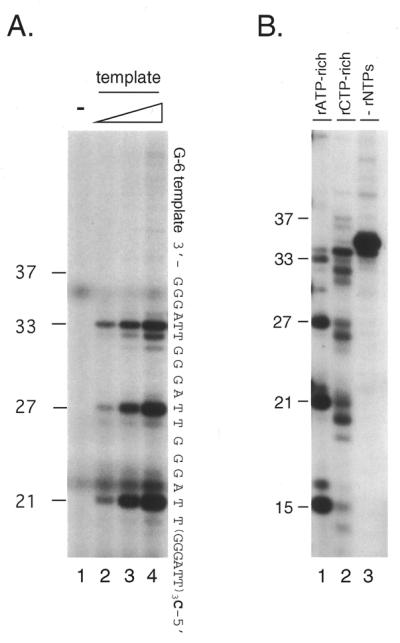
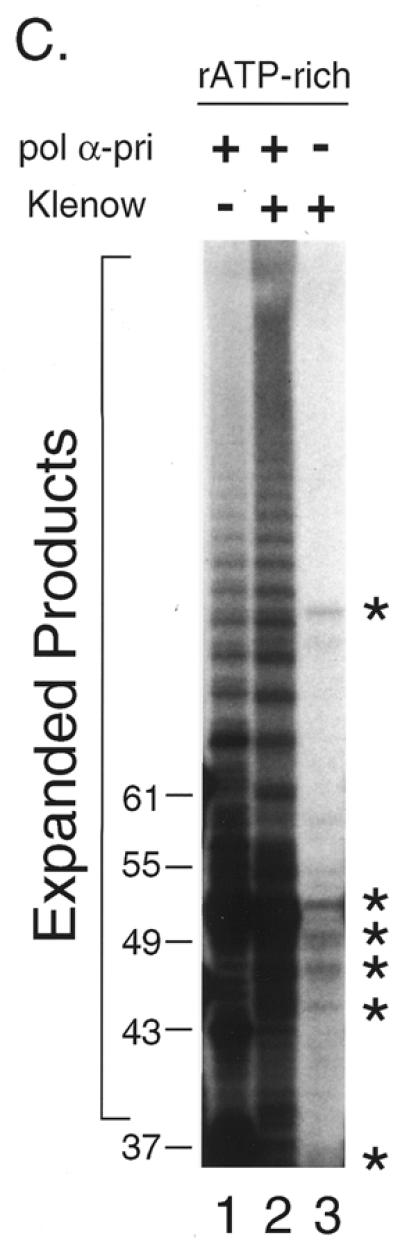
Lagging strand synthesis by pol α-primase on the telomere G-rich strand. (A) Initiation of RNA primer synthesis at a specific sequence. Reactions were performed with four dNTPs and four rNTPs using 0.08 U pol α-primase as described in Materials and Methods (rATP-rich conditions). As templates, 0, 10, 50 and 100 ng G-6 template were used (lanes 1–4, respectively). The reaction products, primer RNA–DNA conjugates, labeled with [α-32P]dGMP at the 3′-end of the DNA, were resolved by denaturing PAGE to show the initiation sites. The sequence of the G-6 template, constructed to incorporate dGMP at the 3′-end, as well as the positions of size markers are indicated. Numbers on the left side of panels indicate products sizes. (B) Shift of initiation sites by changing the ratio of rNTPs. Reactions were performed as described for (A) except that, in addition to rATP-rich conditions (lane 1), rCTP-rich conditions were employed (lane 2) using 100 ng G-6 template and 0.16 (lane 1) or 0.32 U (lane 2 and 3) pol α-primase (Materials and Methods). Reactions without rNTPs were performed as a negative control (lane 3). Sizes of the products are indicated on the left side of the figure. (C) Expansion of RNA-primed DNA products on the G-rich telomere strand by pol α-primase. The rNTPs-dependent DNA synthesis reaction was performed under rATP-rich conditions with 100 ng G-6 template and 1.6 U pol α-primase (lane 1). As a positive control for expansion, 1.0 U Klenow fragment was further added (lane 2). As a negative control (lane 3), primase (pol α-primase) was omitted from the reaction mixture used for lane 2. Products were labeled with [α-32P]dGTP at the 3′-ends of the the DNA that was extended from RNA primers and their sizes were estimated from positions of 32P-labeled oligonucleotides. The asterisks indicate non-specific products.
