Figure 13.
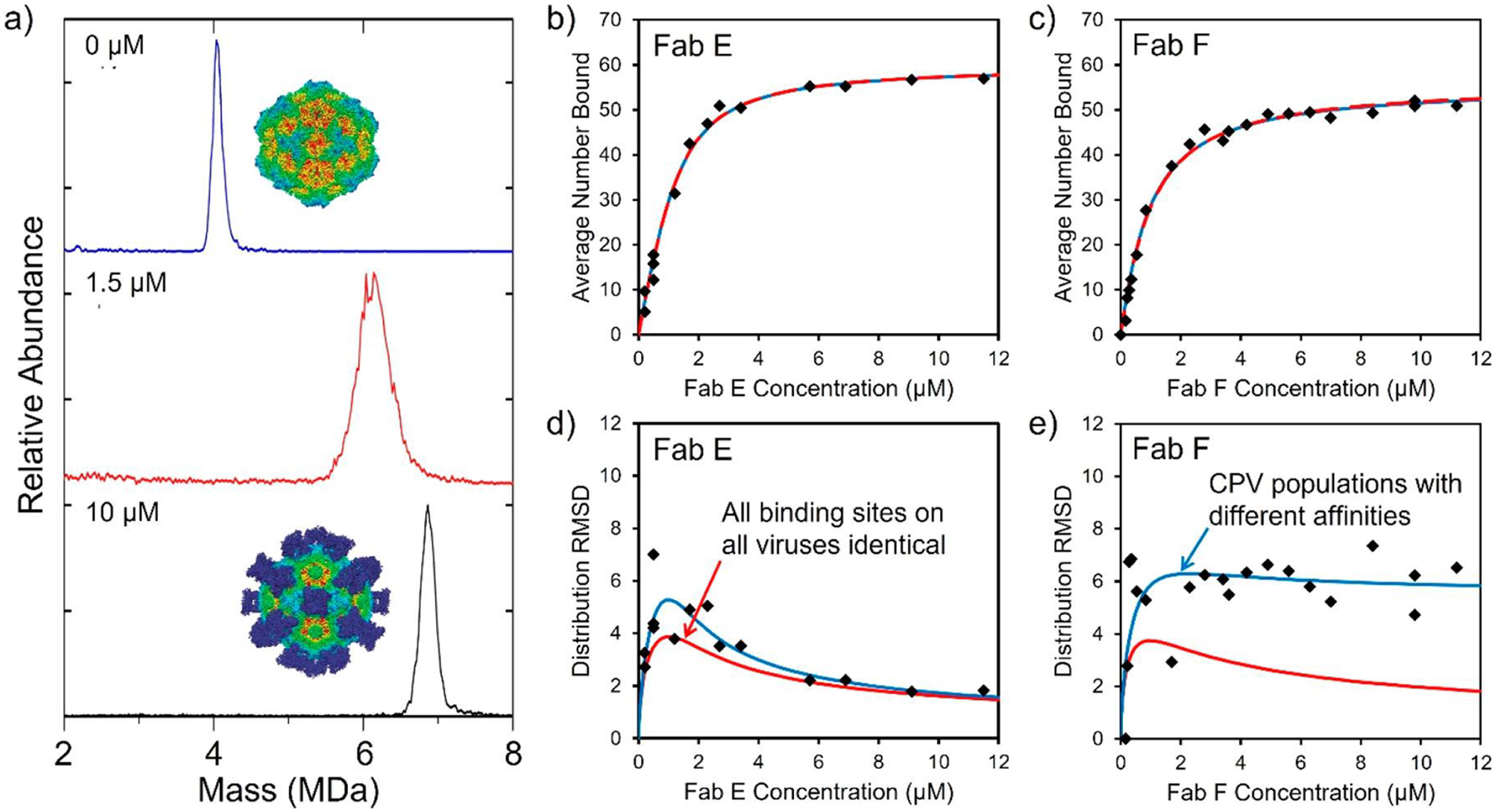
Fab binding to CPV capsids. (a) Mass distributions measured for CPV at FAB E concentrations of 0, 1.5, and 10 μM. The average mass shift provides information on the average number of Fabs bound, and the peak width provides information on the distribution of bound Fabs. The insets show cryo-EM images of CPV without Fabs (top) and saturated with 60 Fabs (bottom). (b) Plot of the average number of Fab E bound to CPV as a function of Fab E concentration. (c) Similar plot for Fab F. The black points are the measured values determined by CDMS. (d) Width of the Fab E distribution plotted against the Fab E concentration. (e) Similar plot for Fab F. The red lines show the predictions of the standard (Langmuir) model for ligand binding, where all sites have the same intrinsic affinity. The blue lines show the prediction of a model where there are CPV subpopulations with different affinities. In (b) and (c) the red and blue lines are coincident. Adapted with permission from ref 256. Copyright 2018 American Chemical Society.
