Fig. 7.
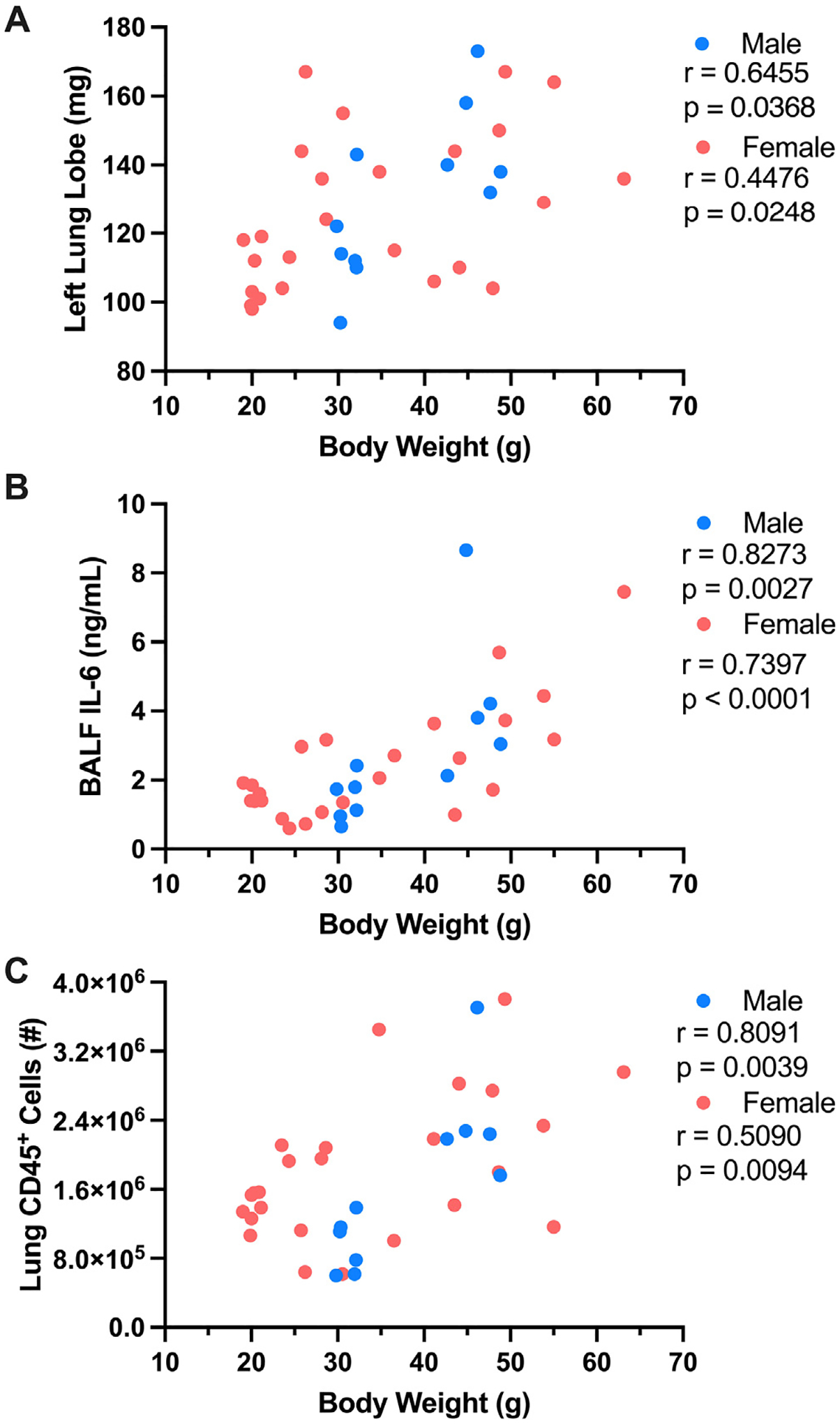
Increased total body weight correlates with worsened influenza-associated disease severity outcomes. Preinfection total body weight in TN-housed lean and obese males and females was correlated with various influenza disease severity metrics. (A) Preinfection total body weight versus left lung weight at 5 DPI. (B). Preinfection total body weight versus bronchoalveolar lavage fluid interleukin-6 levels at 5 DPI. (C) Preinfection total body weight versus Lung CD45+ immune cell infiltration at 5 DPI. Nonparametric Spearman Rank Correlation and Pearson Correlation tests were performed for males and females, respectively, performed in Prism (GraphPad software). R and p values directly reported. DPI = days post-infection; TN = thermoneutral.
