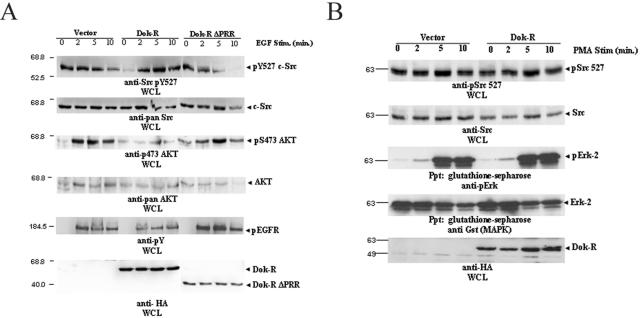
FIG. 4.
(A) Overexpression of Dok-R facilitates EGF-dependent hyperphosphorylation of autoinhibitory Src Y527. Serum-starved Cos1 cells transfected with either vector Dok-R or Dok-R ΔPRR were either left unstimulated (lane 0) or stimulated (Stim.) with EGF at 100 ng/ml (2, 5, or 10 min) for the indicated times. Cleared lysates were prepared and subjected to SDS-PAGE. Immunoblot analysis of WCL demonstrates that overexpression of Dok-R but not vector or Dok-R ΔPRR results in an EGF-dependent hyperphosphorylation of Src on tyrosine 527. These results cannot be accounted for by overall Src levels (anti-Src immunoblot) or differences in EGFR activation (anti-pY EGFR). Coincident with the Dok-R-dependent hyperphosphorylation of Src Y527 is a dramatic decrease in Akt activation (anti-Akt pS 473), which cannot be accounted for by overall Akt protein levels (anti-pan-Akt). (B) Dok-R does not inhibit Src kinase or MAPK activation in response to PMA stimulation. Cos1 cells cotransfected with one of either vector or Dok-R and GST-Erk2 were left unstimulated (lane 0) or stimulated for indicated times (2, 5, and 10 min) with 200 nM PMA. Cleared lysates were prepared and subjected to SDS-PAGE. Immunoblot analysis demonstrates that overexpression of Dok-R does not result in PMA-dependent inhibition of Src kinase activity (anti-Src pY527) or MAPK activation (Gst Ppt/anti-pErk) when compared to vector-transfected cells.