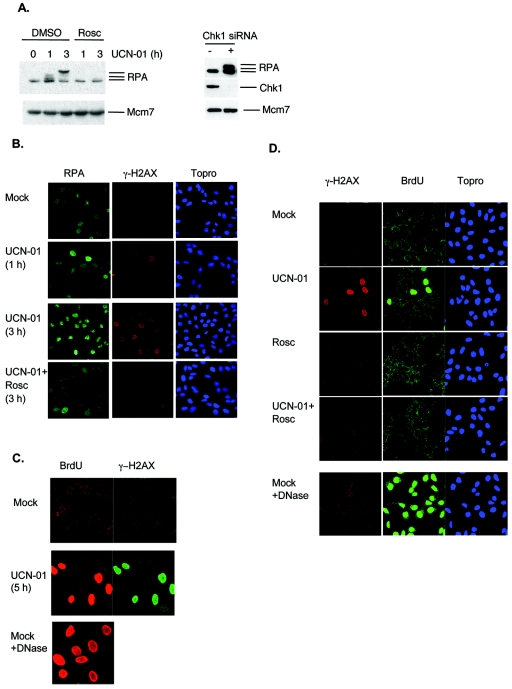
FIG. 4.
Chk1 inhibition causes formation of ssDNA. (A) Increased levels of nonextractable RPA protein after Chk1 inhibition. U-2-OS cells were treated with UCN-01 (300 nM) for 0, 1, or 3 h in the absence or presence of roscovitine (25 μM; left panel) or transfected with control (−) or Chk1 (+) siRNA (100 nM, 48 h; right panel), incubated with extraction buffer, and processed for Western blotting. Mcm7 protein is a loading marker. (B) U-2-OS cells were treated with UCN-01 (300 nM) in the absence or presence of roscovitine (25 μM), incubated with extraction buffer, and stained with antibodies to RPA and γ-H2AX and the DNA stain Topro3. (C) Detection of incorporated BrdU in the absence of DNase treatment after Chk1 inhibition. U-2-OS cells prelabeled with BrdU were treated with UCN-01 (100 nM) for 5 h and stained with antibodies to BrdU and γ-H2AX. DNase-treated cells are included to show that the whole-cell population was labeled with BrdU. (D) Roscovitine inhibits the formation of ssDNA. U-S-OS cells prelabeled with BrdU were treated with UCN-01 (300 nM) for 3 h and stained with antibodies to BrdU and γ-H2AX and with the DNA stain Topro3. DNase-treated sample is included to show incorporation of BrdU.