Figure 9. Neonatal ethanol (EtOH) exposure increased the total charge of spontaneous inhibitory postsynaptic currents (sIPSCs) in retrosplenial cortex-projecting anterodorsal (AV) thalamic nucleus neurons at postnatal days 40–60.
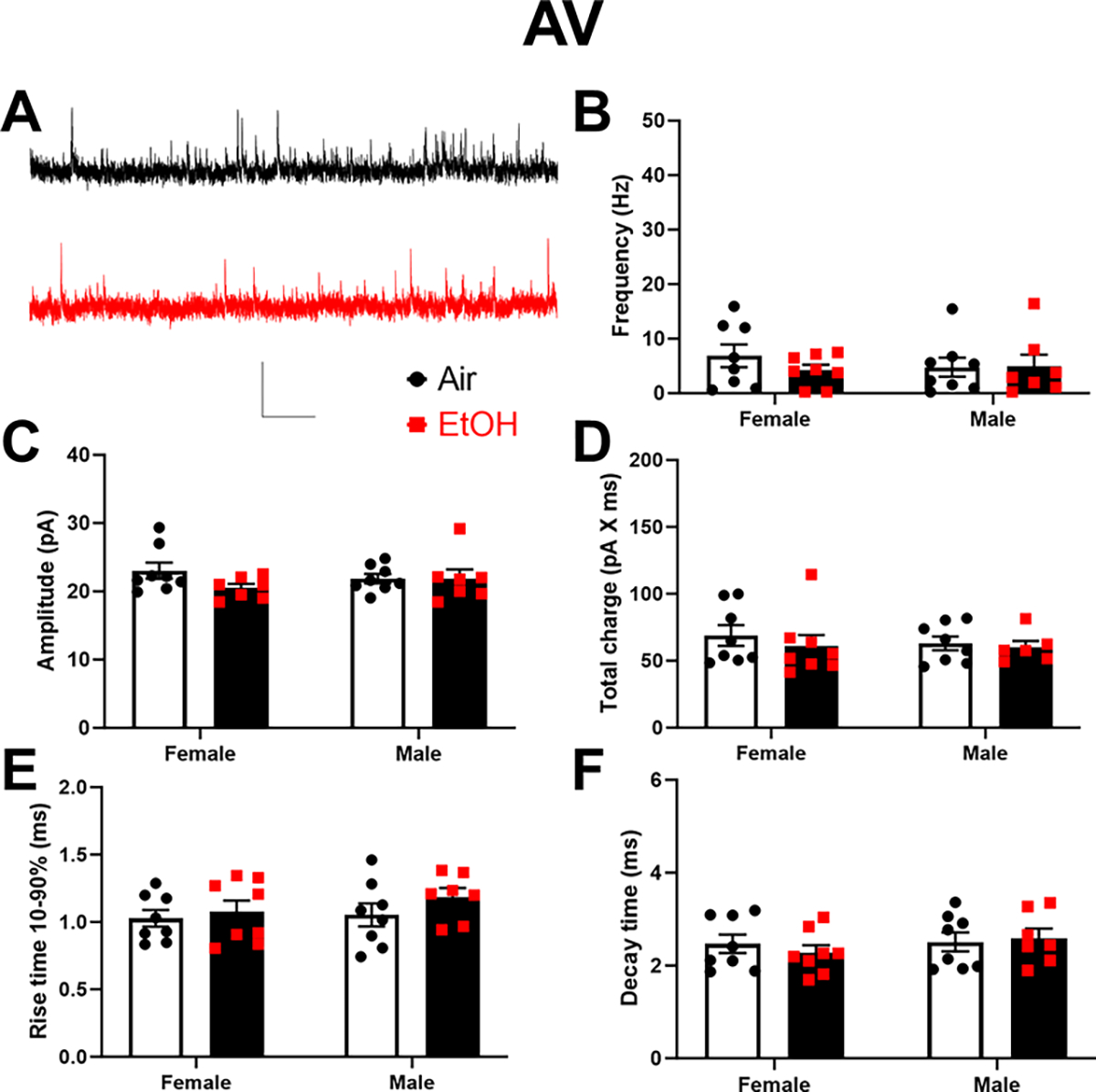
A) Representative sIPSC traces from the Air (control) (black trace) and EtOH groups (red trace). Scale bar is 0.4 s X 40 pA. B) Mean effect of EtOH exposure on sIPSC frequency. C) Mean effect of EtOH exposure on sIPSC amplitude. D) Mean effect of EtOH exposure on sIPSC total charge. E) Mean effect of EtOH exposure on sIPSC rise time 10–90%. F) Mean effect of EtOH exposure on sIPSC decay time. Control female, n=8 pups from 6 litters; EtOH female, n=8 pups from 6 litters; control male, n=8 pups from 5 litters; EtOH male, n=7 pups from 6 litters.
