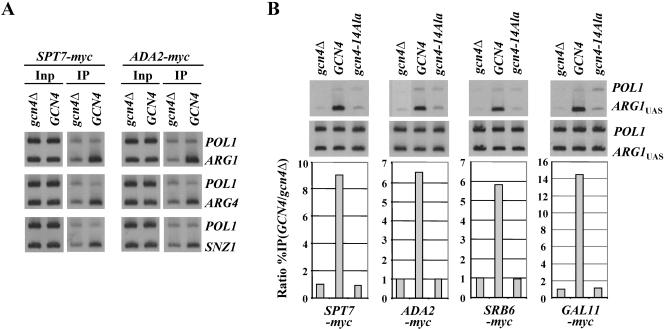
FIG. 1.
Gcn4p recruits myc-Spt7p, myc-Ada2p, myc-Srb6p, and myc-Gal11p, dependent on hydrophobic residues in the activation domain. (A) SPT7-myc gcn4Δ and ADA2-myc gcn4Δ strains bearing empty vector (gcn4Δ) and SPT7-myc GCN4 and ADA2-myc GCN4 strains carrying high-copy-number GCN4-HA plasmid pHQ1239 were cultured in SC medium lacking Ile and Val and treated with sulfometuron for 2 h to induce Gcn4p synthesis by starvation for Ile/Val and then subjected to ChIP analysis with myc antibodies. DNA was extracted from the immunoprecipitates (IP), and 5% of the input (Inp) samples and a 1,000-fold dilution of the Inp and the undiluted IP DNA samples were PCR amplified using primers specific for the POL1ORF, ARG1UAS, SNZ1UAS, or ARG4 promoter (UAS and TATA sequence), in the presence of [33P]dATP. The PCR products were resolved by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and visualized by autoradiography. (B) The SPT7-myc gcn4Δ and ADA2-myc gcn4Δ strains described above, along with SRB6-myc gcn4Δ and GAL11-myc gcn4Δ strains, bearing empty vector (gcn4Δ), high-copy-number GCN4 plasmid pHQ1303 (GCN4), or high-copy-number gcn4-14Ala plasmid pHQ1304 (gcn4-14Ala), were subjected to ChIP analysis as above, and the results were quantified with a phosphorimager. The ratios of the ARG1UAS signals to the POL1 signals in the IP samples were normalized for the corresponding ratios for the Inp samples, and the resulting values measured for the GCN4 strain were normalized to the corresponding values obtained for the gcn4Δ strain to produce the “ratio %IP(GCN4/gcn4Δ)” values plotted in the histograms for each protein.