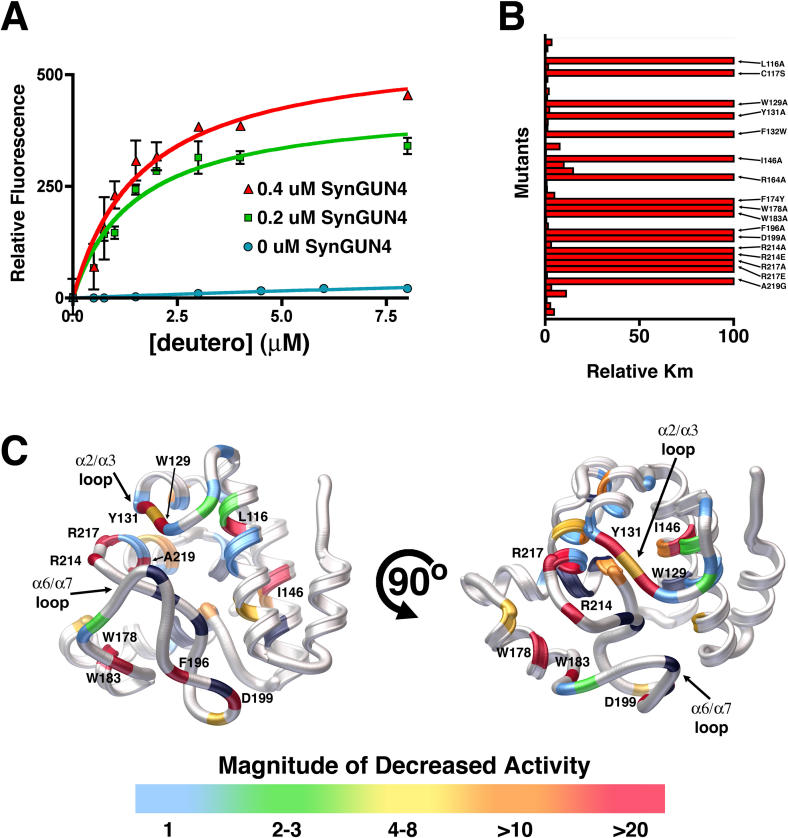
Figure 7. Quantitative Analysis of the GUN4 Stimulation of Mg2+ Incorporation into Deutero.
(A) The K m values for GUN4 assisted Mg-Deutero biosynthesis were determined using both 0.2 μm (red) and 0.4 μM SynGUN4 (green). The resultant values contrast with those obtained for Mg2+ incorporation by the Mg-chelatase complex in the absence of SynGUN4 (blue).
(B) Relative K m values (compared to wild-type SynGUN4) were determined for each SynGun4 mutant previously examined for Deutero binding.
(C) Rendered ribbon diagrams of orthogonal views of the SynGUN4 core domain with the relative K m values of each SynGUN4 mutant mapped onto the structure. The color-coded scale for each mutation's effect on Mg2+ incorporation is shown at the bottom. Several mutants that altered Mg2+ incorporation activity but previously did not affect binding to deuteroporphyrin IX were uncovered including a R217A mutation and the Trp129 and Tyr131 residing on the α2/α3 loop. Mutants of Val218, the later of which is critical for binding Deutero but not for binding Mg-Deutero showed no effect on chelatase activity while mutants of Ala219, the later of which is essential for binding to Mg-Deutero, completely failed to stimulate Mg-chelatase activity. Only those mutant SynGUN4s exhibiting a greater than 10-fold change in K m are labeled. Shown in black are residues that, when mutated to alanine, failed to produce properly folded protein upon expression in E. coli.