Figure 2. Conserved catalytic cycle of glutathione peroxidases.
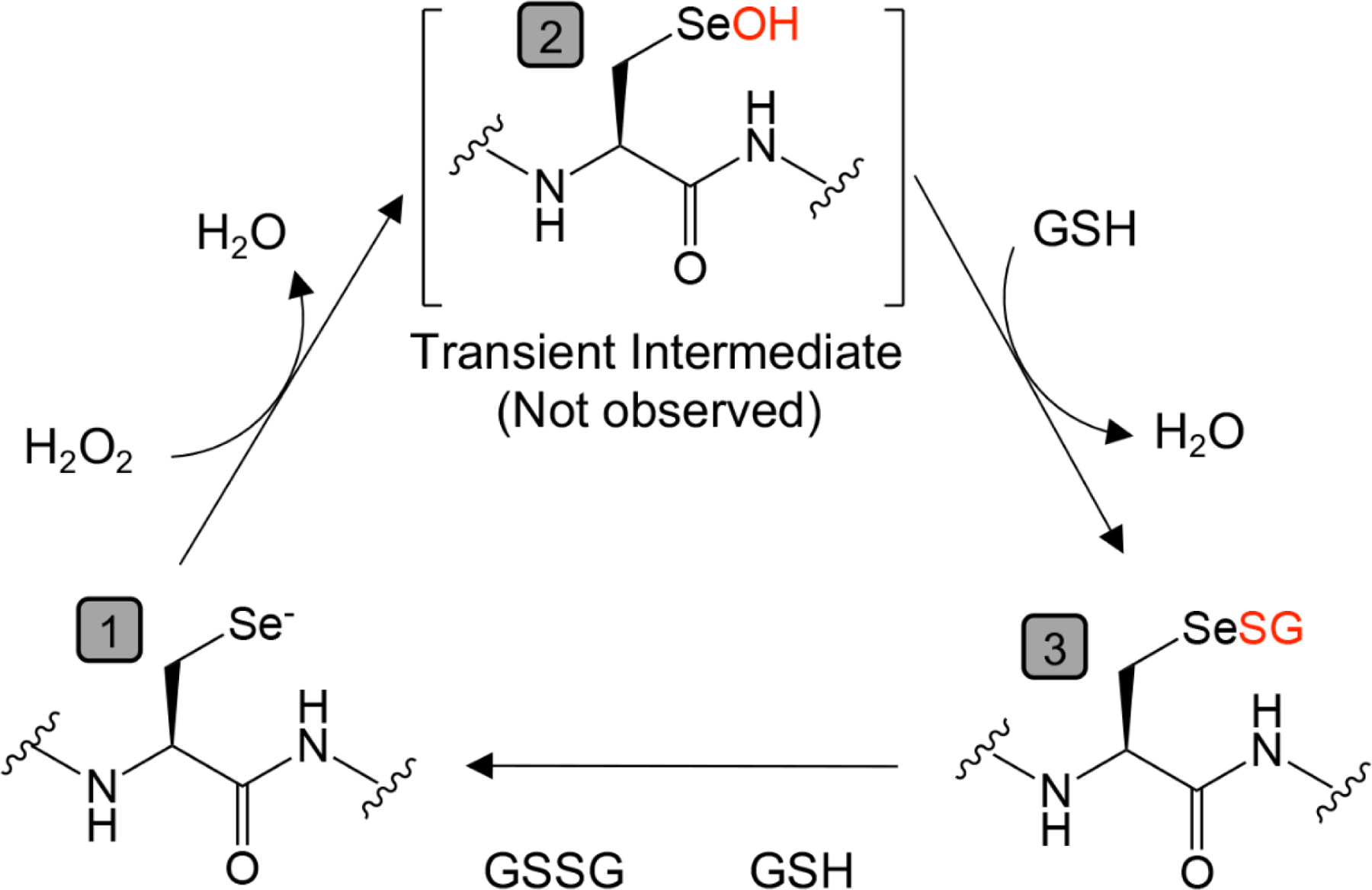
Starting from (1), the catalytic selenocysteine exists in a base state as a selenol (Se−) which quickly reacts with hydrogen peroxide to generate (2) selenenic acid (SeOH), a temporary intermediate that is rapidly replaced by reduced glutathione (GSH) to form (3) a selenenyl sulfide adduct (SeSG). The enzyme is subsequently regenerated to (1) through its reaction with a second GSH, resulting in the production of oxidized glutathione (GSSG).
