Figure 1.
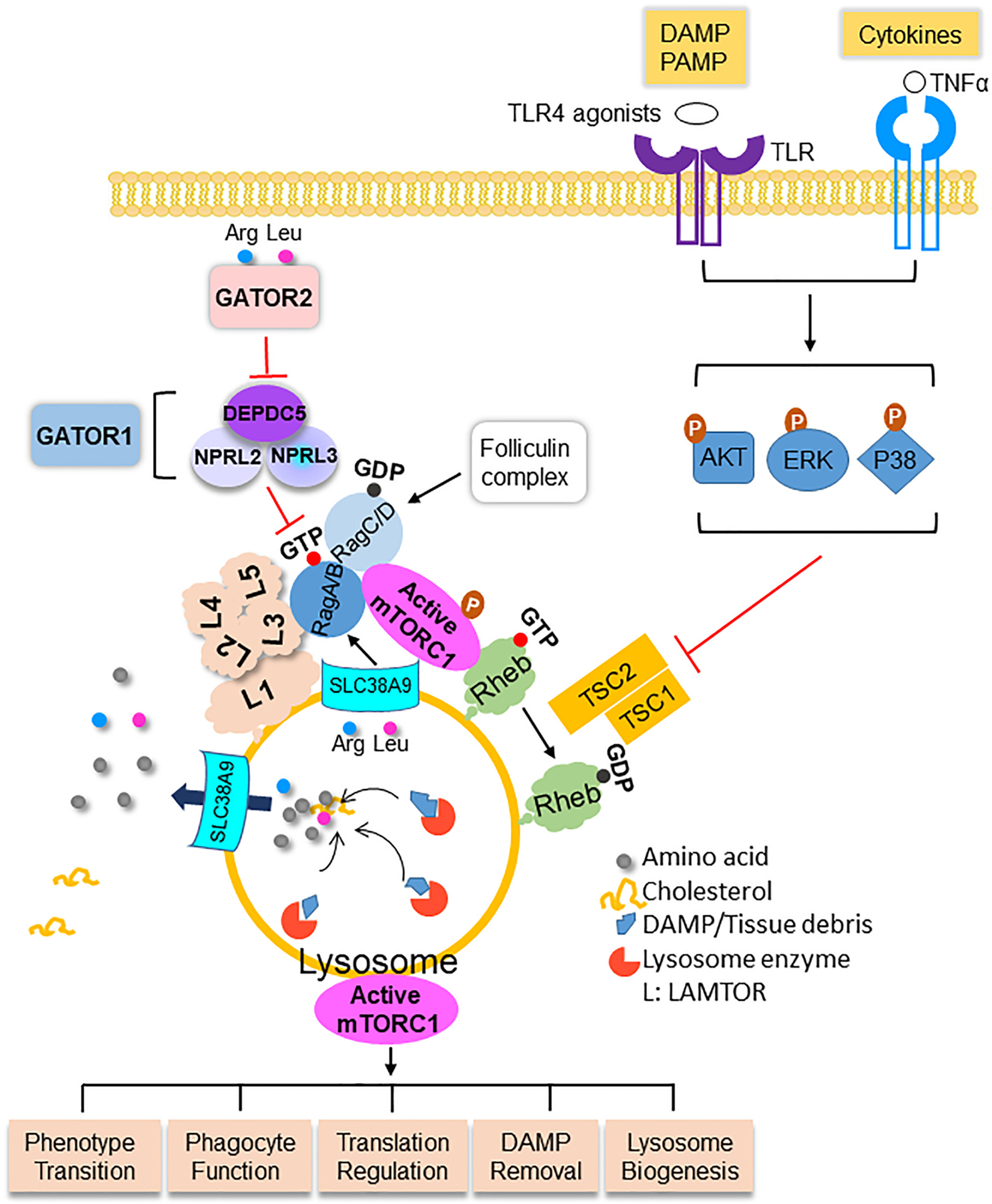
The architecture of mTORC1, the activation and the role of mTORC1 in macrophages in myocardial ischemia. Macrophages digest DAMP/tissue debris to generate amino acids. Amino acids are transported out of lysosomes into the cytosol where arginine (Arg) and leucine (Leu) trigger the translocation of mTORC1 to the surface of lysosomes via Rag GTPase. The LAMTOR (L) complex anchors mTORC1-Rag to the lysosome membrane. Arginine inside the lysosome activates mTORC1 after being sensed by SLC38A9. The assembly of mTORC1 on lysosome membrane is inhibited by GATOR1 and promoted by GATOR2. mTORC1 in macrophages in the infarcted myocardium is activated by the interaction between DAMP and PRR, including TLR4 and its ligands, and cytokines such as TNFα. The stimulation of DAMP and cytokine lead to the activation of AKT, MAPK/ERK, and P38, which phosphorylate the TSC complex. Phosphorylated TSC relieves its inhibitory effect on Rheb that causes activation of mTORC1. mTORC1 regulates essential functions of macrophages including phenotype transition, phagocytotic function, translational regulation of cytokines, DAMP removal, and lysosome proliferation and action. More details are discussed in the main text. DAMP, damage-associated molecular pattern; PRR, pattern recognition receptor; PAMP, pathogen-associated molecular pattern
