Fig. 2.
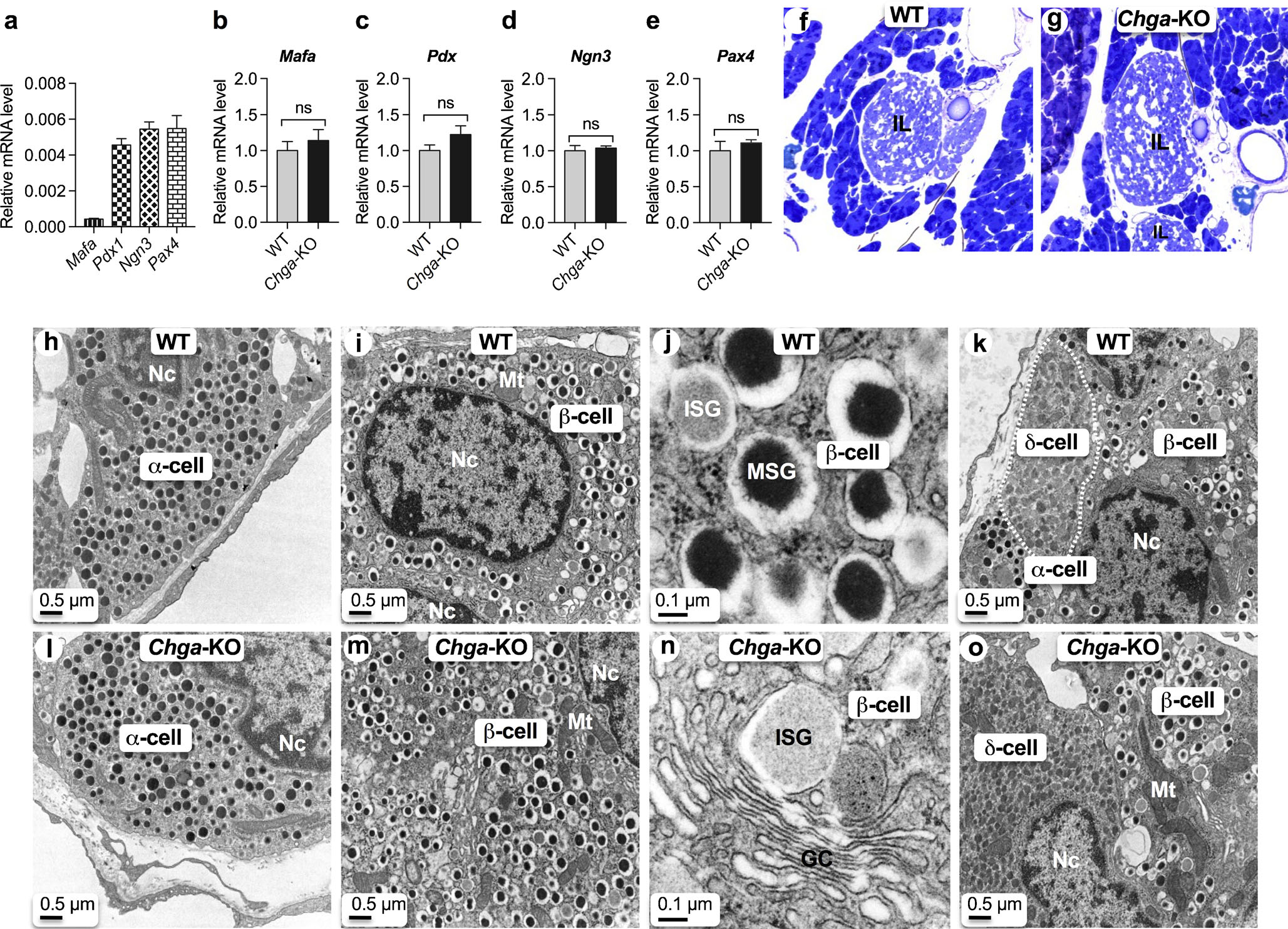
CgA does not influence ontogenesis and differentiation of pancreatic islets. qRT-PCR data showing expression of transcription factor genes (n = 6). a Basal expression in WT islets; b Mafa mRNA levels in WT and Chga-KO islets; c Pdx1 mRNA levels in WT and Chga-KO islets; d Ngn3 mRNA levels in WT and Chga-KO islets; e Pax4 mRNA levels in WT and Chga-KO islets. f, g Toluidine blue-stained section of pancreatic islets: f WT; g Chga-KO. h–o Transmission electron microscopic (TEM) images of the pancreatic islets: h α-cell in WT islet; i α-cell in Chga-KO islet; j β-cell in WT islet; k β-cell in Chga-KO islet; l higher magnification images of a β-cell showing ISG and MSG; m higher magnification images of a β-cell showing Golgi complex and budding off an ISG from the middle of a Golgi stack; n β- and δ-cells (marked by white dotted line) in WT islet; o β- and δ-cells (marked by dotted line) in WT islet. GC Golgi complex, ISG immature secretory granule, MSG mature secretory granule, Mt mitochondria, Nc nucleus, ns not significant
