Fig. 1. Deficiency of miR-9-1 reduces overall mature miR-9 expression and causes growth defect and white blood cell reduction with incomplete penetrance.
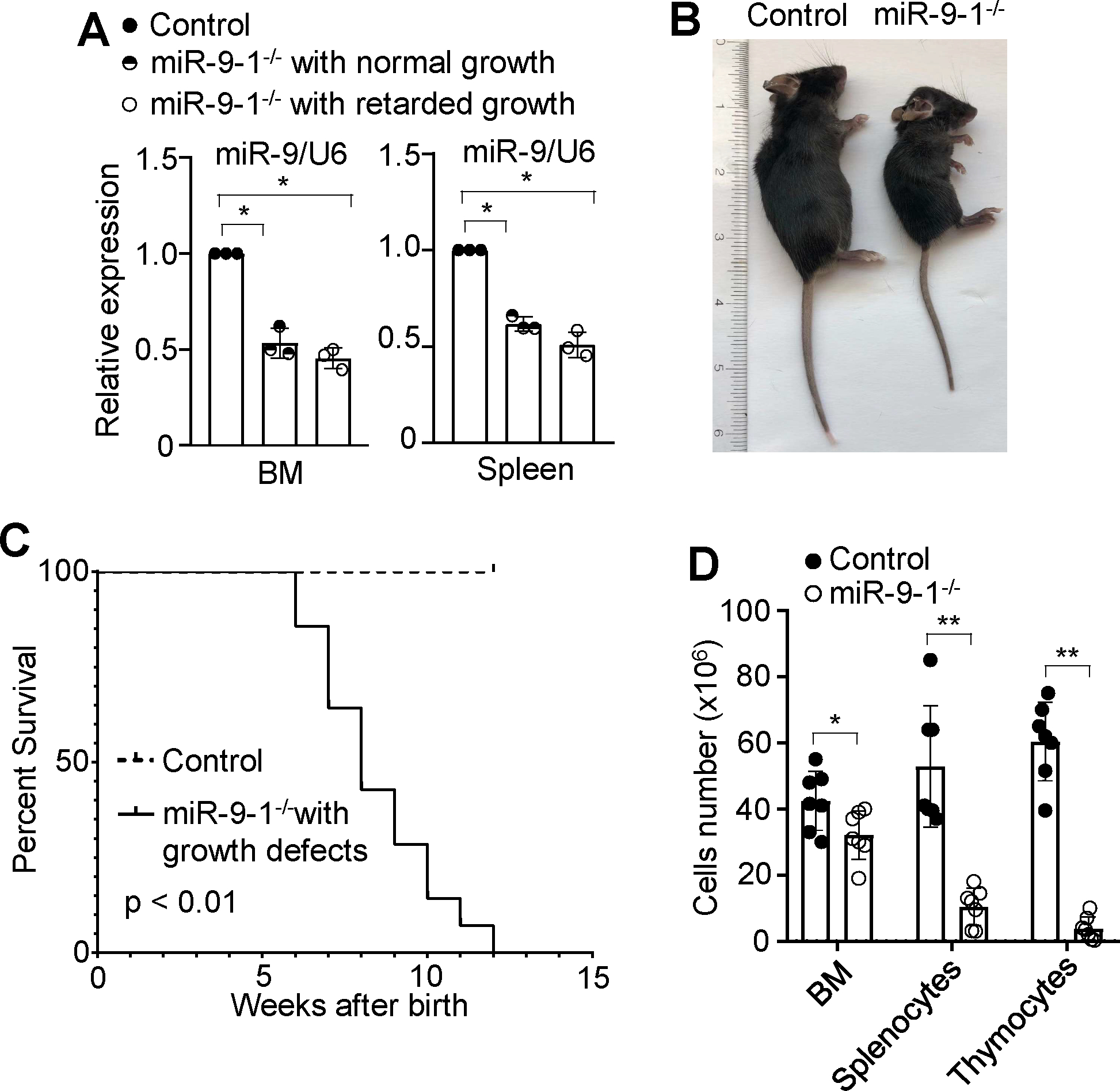
A Reduction in overall mature miR-9 expression in the BM and splenic cells from miR-9-1-deficient mice. The levels of mature miR-9 expression in BM and splenic cells from miR-9-1-deficient (miR-9-1−/−) mice with normal or retarded growth were quantified by qRT-PCR as a fraction of the corresponding wild-type control cells, which was set as 1. B Growth defect of miR-9-1-deficient mice. A representative image of 8-week-old growth-retarded male miR-9-1−/− mice and controls is shown. C Cumulative survival curve of miR-9-1-deficient mice with retarded growth. D Numbers of total BM cells, splenocytes and thymocytes in growth-retarded miR-9-1-deficient and control mice. Data shown are representative of or obtained from 3 independent experiments (A), and 9 (B, C) and 7 (D) pairs of wild-type control and growth-retarded miR-9-1−/− mice. Mean ± SD is shown. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.
