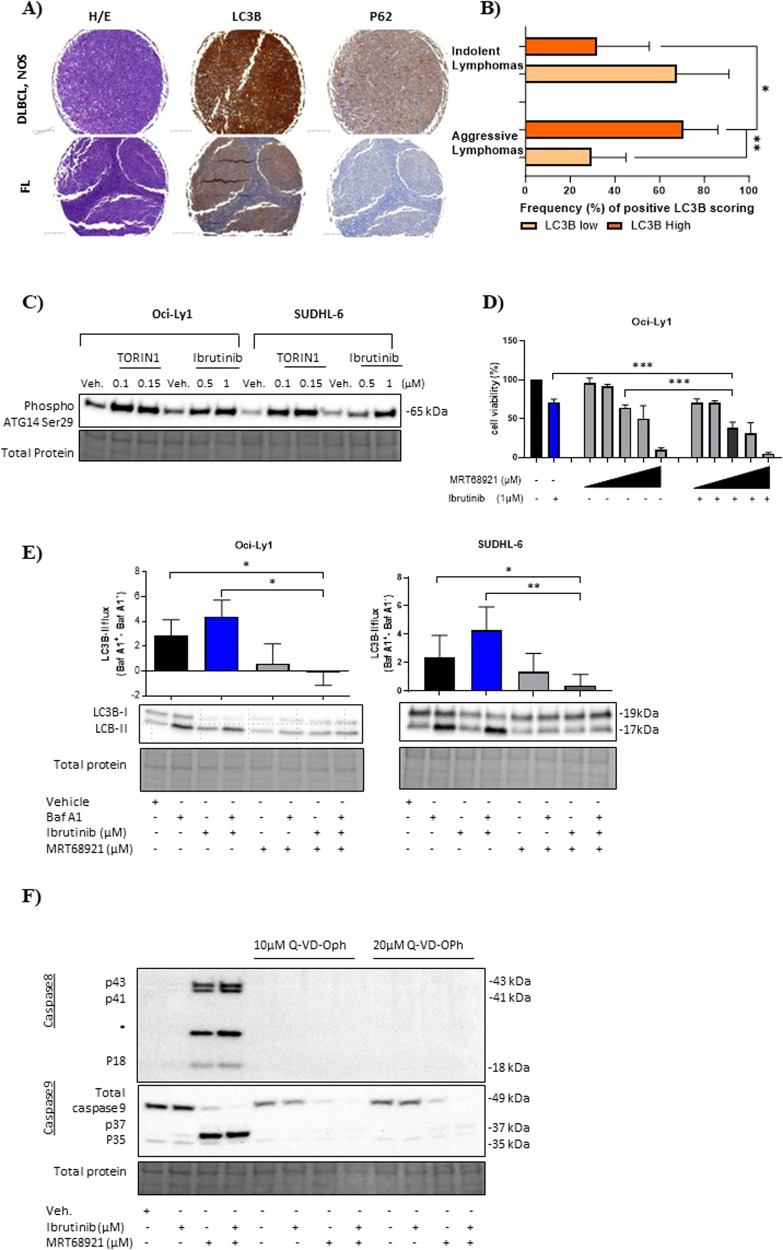
Fig. 1. Characterisation of autophagy dependency in primary lymphomas and its preferential targeting in GCB-DLBCL cell lines.
A Representative images of immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining of excised lymph nodes from aggressive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL, NOS) (top) and follicular lymphoma (FL) (bottom) (10X). Upper and lower lymphoma panel view of autophagy markers: LC3B and p62, and haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining. Left panel view of haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining, middle and right panels are stained for LC3B and p62. Intense cytoplasmic staining for LC3B and p62 (brown colouration) was defined in DLBCL, NOS compared to FL. B 318 primary lymphoma cases were grouped according to their clinical classifications being indolent (n = 149) and aggressive (n = 169) lymphomas (Supplementary Fig. 1B defines the classification of lymphoma entities). Bar graph summarising the LC3B staining positivity (%) of indolent and aggressive lymphomas. Unpaired student t test two-tailed test was used for statistical analysis. C Representative blot of two independent experiments for GCB Oci-Ly1 and SUDHL-6 cells treated with vehicle, TORIN1 (0.1 and 0.15 µM) and ibrutinib (0.5 and 1 µM) for 4 h. D Cell viability assessment of GCB Oci-Ly1 was subjected to vehicle, ibrutinib (as indicated), ascending MRT68921 (0.5, 1, 2.5, 3 and 5 µM) concentrations in combination for 24 h. P values were calculated using one-way ANOVA and Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test, and student t test between variables. E GCB Oci-Ly1 and SUDHL-6 was treated with vehicle, ibrutinib, MRT68921 and in combination for 24 h in the presence and absence of bafilomycin A1 (Baf A1, 0.2 µM) in the last 2 h. Statistical significance was determined using Mann-Whitney U test. F Representative image of Oci-Ly1 treated with vehicle, ibrutinib (1 µM), MRT68921 (2.5 µM) and combination in presence and absence of pan-caspase inhibitor Q-VD-OPh (10 and 20 µM) for 8 h (two independent experiments). Activation of caspase 8 was determined through the engagement of cleavage p43, p41 and active p18. Caspase 9 was activated through cleavage p37 and p35. In the presence of Q-VD-OPh caspase cleavages were abolished. *Non-specific protein. Representative error bars of mean ± SD, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.