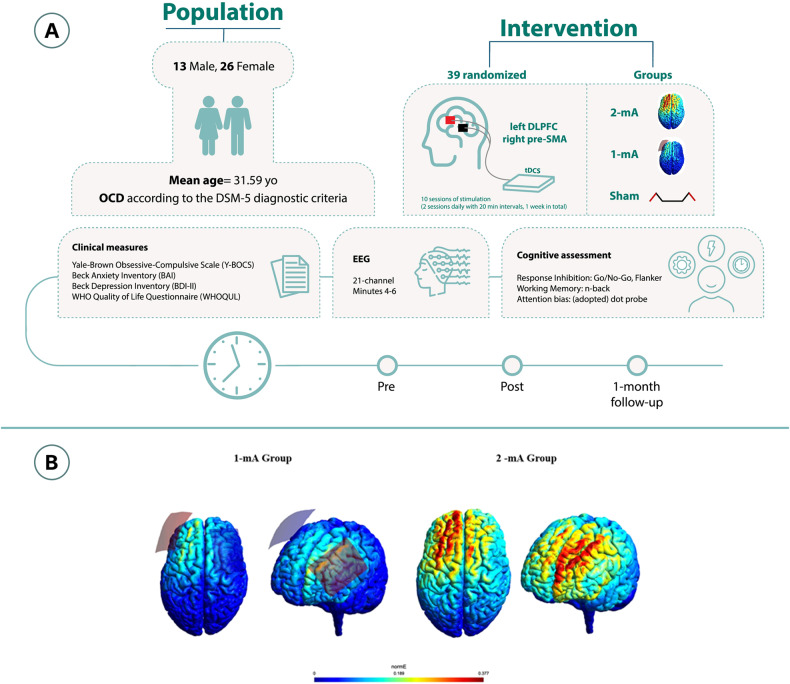
Fig. 2. Study procedure and the intervention.
A The experiment was conducted in a randomized, double-blind, sham-controlled parallel-group design. Participants were randomized to 3 tDCS arms: 1-mA tDCS (n = 12), 2-mA tDCS (n = 13), and sham tDCS (n = 12). B Results of the electrical field simulation for the current flow in the head based on the applied protocols. The anodal electrode (red) was placed over the left DLPFC and the cathode (blue) over the pre-SMA (FC2). The induced electric fields (EF) were calculated using SimNIBS [80], an open-source pipeline for Non-invasive Brain stimulation. (NIBS) modeling (available at https://simnibs.github.io/simnibs/). SimNIBS employs the mri2mesh tool, integrating FSL and FreeSurfer, to estimate the EF distribution. FSL segments extracerebral tissues, while FreeSurfer handles brain segmentation and gray matter surface reconstructions. Simulations were performed for the MNI-152 standard head [81]. Two stimulation protocols were modeled: one with 7 × 5 cm electrodes over the left DLPFC (F3) and the pre-SMA (FC2), with 1-mA current intensity, and the same parameters except for the intensity, which was 2-mA (10–20 EEG electrode positioning system). The average EF value (undirected) in each region was calculated based on the sum of EF values and the number of voxels in the area. All the calculations were performed using FSL and Matlab.