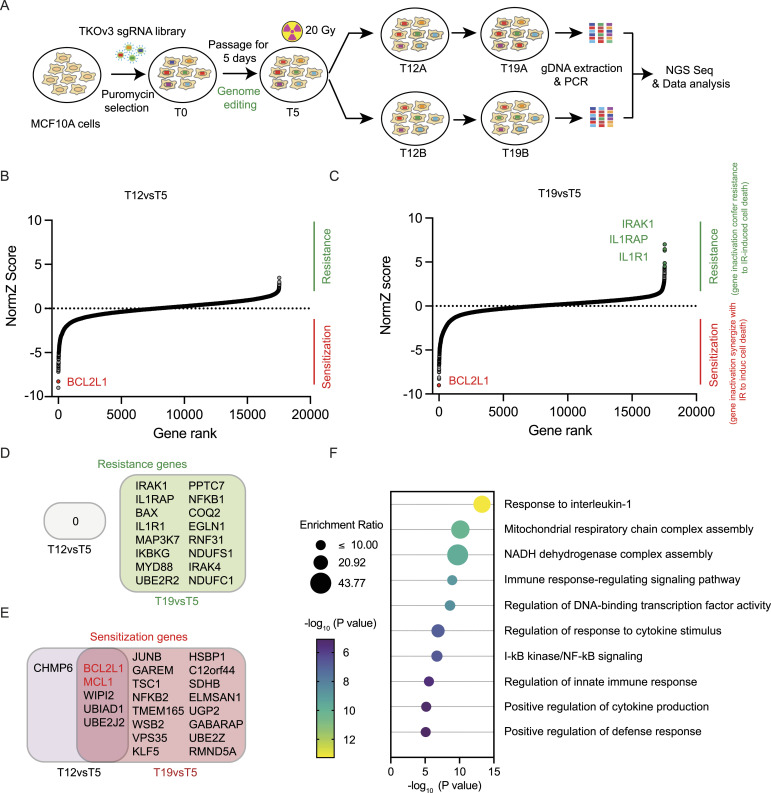
Figure 1. Genome-wide CRISPR/Cas9 screens in MCF10A cells with a single high dose of radiation.
(A) Schematic of the workflow for CRISPR screen in MCF10A cells treated with radiation and the TKOv3 whole-genome gRNA library. Cells infected with the TKOv3 library virus were cultured and passaged after puromycin selection. At day 5, all cells were treated with 20 Gy of radiation and then divided into two biological replicates. We collected cells at day 5 (T5), day 12 (T12), and day 19 (T19). Genomic DNA extracted from different groups of cells was amplified, sequenced, and analyzed. (B, C) Ranking of the coessential genes based on DrugZ analysis of the screen results. (B) sgRNA read counts from 7 d after radiation (cells at T12) were compared with the read counts from cells at T5 without radiation. (C) sgRNA read counts from 14 d after radiation (cells at T19) were also compared with the read counts from cells at T5 without radiation. Positive NormZ scores suggest that these sgRNAs were enriched in the postradiation group, indicating that they target radiation-sensitizing genes. Likewise, negative NormZ scores suggest that these sgRNAs were depleted in the postradiation groups, indicating that they target radiation-resistant genes. (D) Overlay of the genes whose depletion conferred resistance to radiation between the early (12 d after IR) and late (19 d after IR) periods. (E) Overlay of the genes whose loss led to radiation ensitization between the early (12 d after IR) and late (19 d after IR) periods. (F) Top 10 significantly enriched Gene Ontology (GO) Biological Process terms (P < 0.001) with the high-confidence candidate genes whose loss of function led to radiation resistance in MCF10A cells.