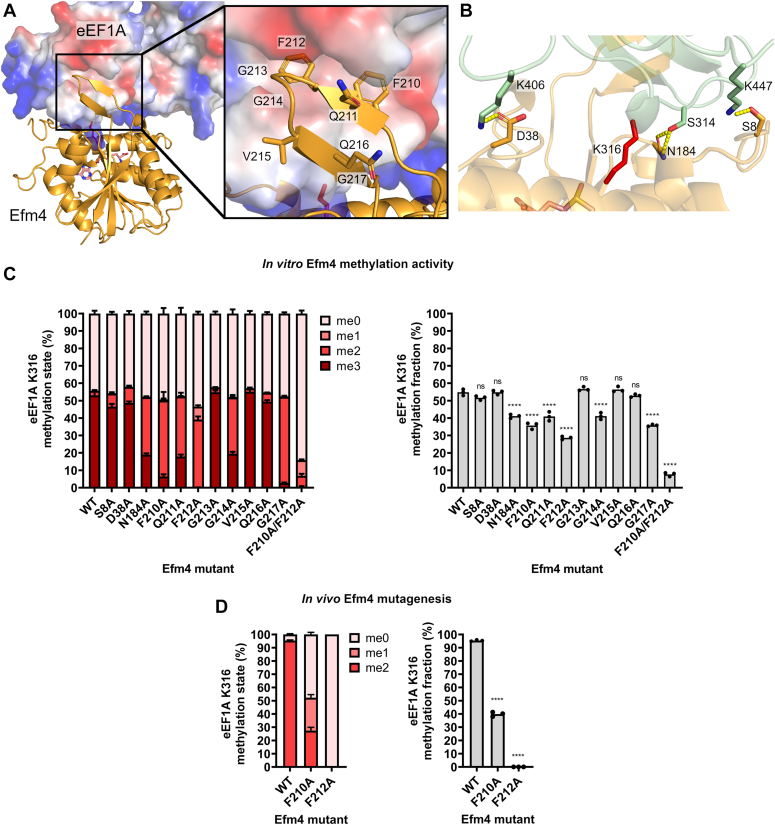
Figure 3.
A beta-hairpin on Efm4 is critical for its activity towards eEF1A K316 in vitro and in vivo.A, AlphaFold-Multimer model of Efm4:eEF1A (rank 1) showing a beta-hairpin extending from Efm4 binding a hydrophobic pocket in domain 2 of eEF1A. Efm4 (orange) is shown as a cartoon structure. eEF1A is shown as its surface electrostatic potential (blue = positive, red = negative, white = neutral). Inset: sidechains of residues on Efm4 beta-hairpin are shown as sticks (nitrogen = blue, oxygen = red). B, model in (A) showing predicted polar contacts between Efm4 (orange) and eEF1A (green). K316 is show as red sticks. Hydrogen bonds are shown as yellow dashes. C, in vitro methylation assays of Efm4 mutants. Purified WT or mutant Efm4 (3 μM) were incubated with eEF1A (from ΔEFM4) (2 μM) in the presence of AdoMet for 30 min at 30 °C. Assays were carried out in triplicate. Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE (see Fig. S8), eEF1A gel bands digested by AspN, and the resulting eEF1A K316 methylation was detected by LC-MS/MS and quantification of AspN-generated peptide DNVGFNVKNVSVK (K316 underlined) in its triply-charged state. Left: Relative levels of eEF1A K316 methylation states. Error bars show one SD. Right: eEF1A K316 methylation fraction relative to 100% trimethylated K316. Methylation fractions from mutant Efm4 were compared to WT Efm4 using an ordinary one-way ANOVA with a post hoc Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test (ns: not significant, ∗∗∗∗p ≤ 0.0001). D, F210A or F212A mutation of Efm4 reduces or ablates eEF1A K316 methylation in vivo. All three clones of WT, F210A, and F212A Efm4 genomic mutants (see Table 1) were analyzed for their levels of eEF1A K316 methylation by parallel reaction monitoring of GluC peptide QGVPGDNVGFNVKNVSVKE (K316 underlined). Left: Relative levels of eEF1A K316 methylation states. Right: eEF1A K316 methylation fraction relative to 100% dimethylated K316. Methylation fractions from mutant Efm4 were compared to WT Efm4 using an ordinary one-way ANOVA with a post hoc Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test (∗∗∗∗: p ≤ 0.0001).