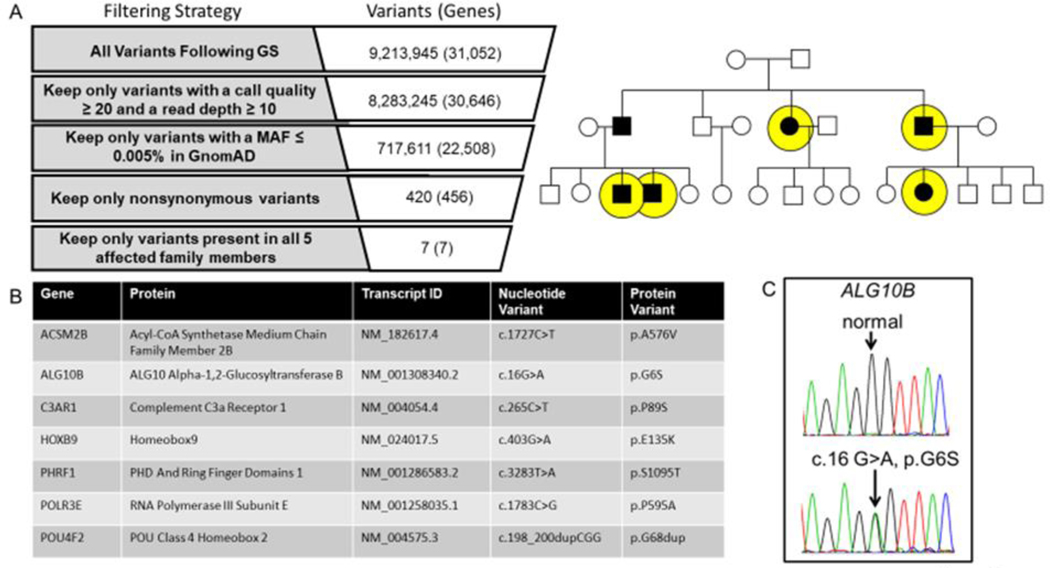
Figure 2 |. Genome sequencing for the identification of a novel pathogenic substrate in an autosomal dominant LQTS pedigree.
Shown in panel A is the genome sequencing variant filtering strategy used to identify ultra-rare non-synonymous candidate variants present in all affected individuals who underwent genome sequencing (yellow circles). Panel B lists the candidate genes/variants that were considered for further analysis. Of the 7 ultra-rare variants, the ALG10B-p.G6S variant represented the top candidate disease causing gene/variant based on biological plausibility. In panel C is the Sanger sequencing chromatogram confirming the c.16G>A (ALG10B-p.G6S) variant.