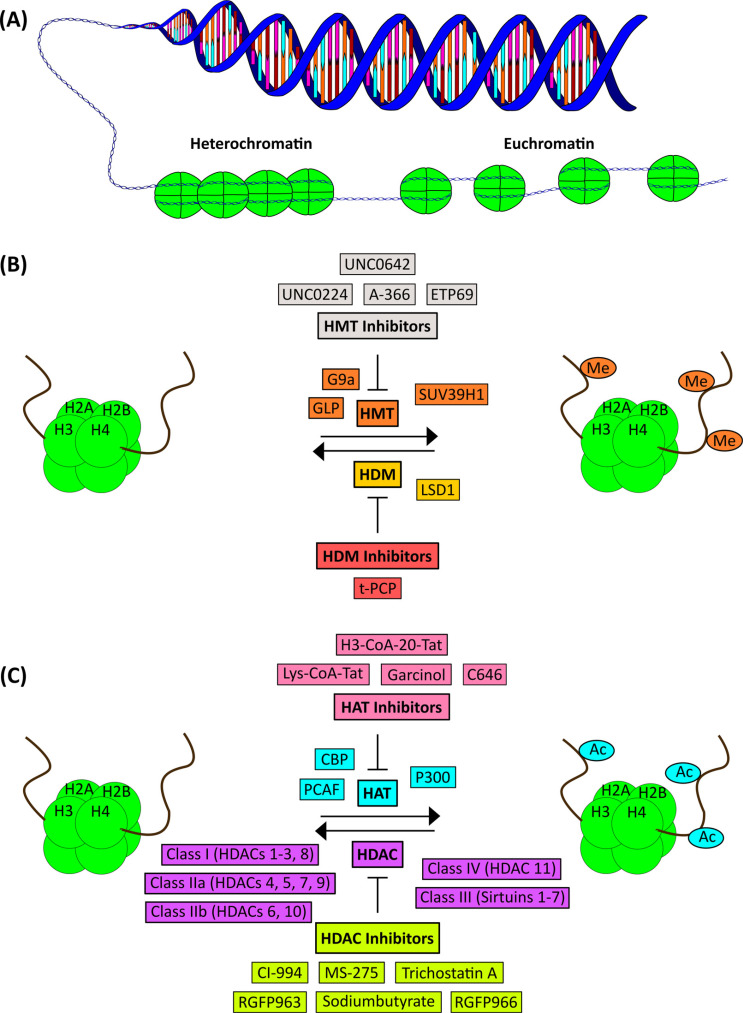
Fig. (1).
Chromatin modifications and regulators targetable by currently available chemical compounds. Schematic illustration of (A) the DNA double-strand wrapped around histone (H2A, H2B, H3, H4) octamers composed of two H2A-H2B dimers and two H3-H4 dimers to form the primary structure of chromatin, which can exist in a compact, i.e. closed state (‘heterochromatin’), or in an open state (‘euchromatin’); (B) mechanisms of histone methylation (HMT: histone methyltransferase) and demethylation (HDM: histone demethylase) as well as exemplary pharmacological HMT and HDM inhibitors; (C) mechanisms of histone acetylation (HAT: histone acetyltransferase) and deacetylation (HDAC: histone deacetylase) as well as exemplary pharmacological HAT and HDAC inhibitors; for further details and abbreviations see main manuscript (1.1. and 3.3.).