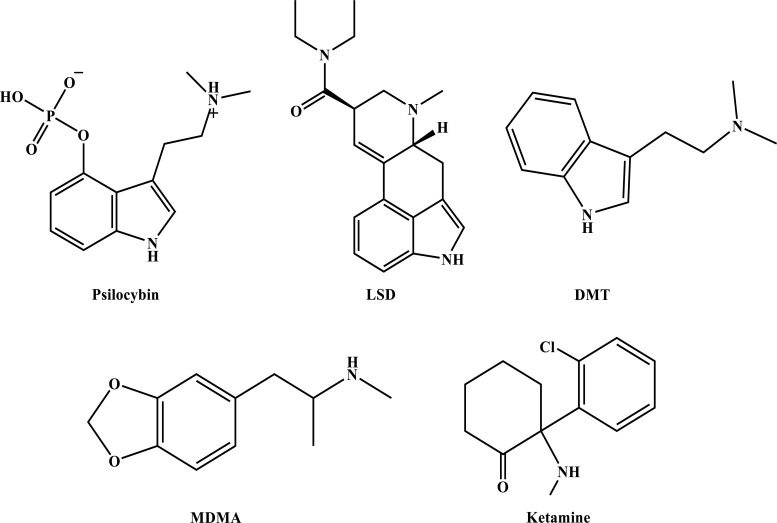
Fig. (2).
Chemical structures of the five psychedelic and psychedelic-like compounds included in this review paper. Classic psychedelics include psilocybin, a tryptophan indole-based alkaloid with a base N,N-dimethyltryptamine structure and an added phosphoryloxy substituent at position 4; lysergic acid diethylamide-25 (LSD), a semisynthetic ergoline composed of an indole system and tetracyclic ring; and N,N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT), the psychoactive component of ayahuasca, a structural analog of tryptamine with two added N-methyl substituents. The entactogen 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) is a ring-substituted phenethylamine that possesses chirality but is typically produced in its racemic form. MDMA has a 2-(methylamino)propyl group at position 5 that is an addition to the base form of 1,3-benzodioxole. The dissociative anesthetic, ketamine, is a racemic mixture composed of two enantiomers, (S)- and (R)-ketamine. Ketamine is a cyclohexanone molecule on which a 2-chlorophenyl group and a methylamino group substitute for the hydrogens typically found at position 2.