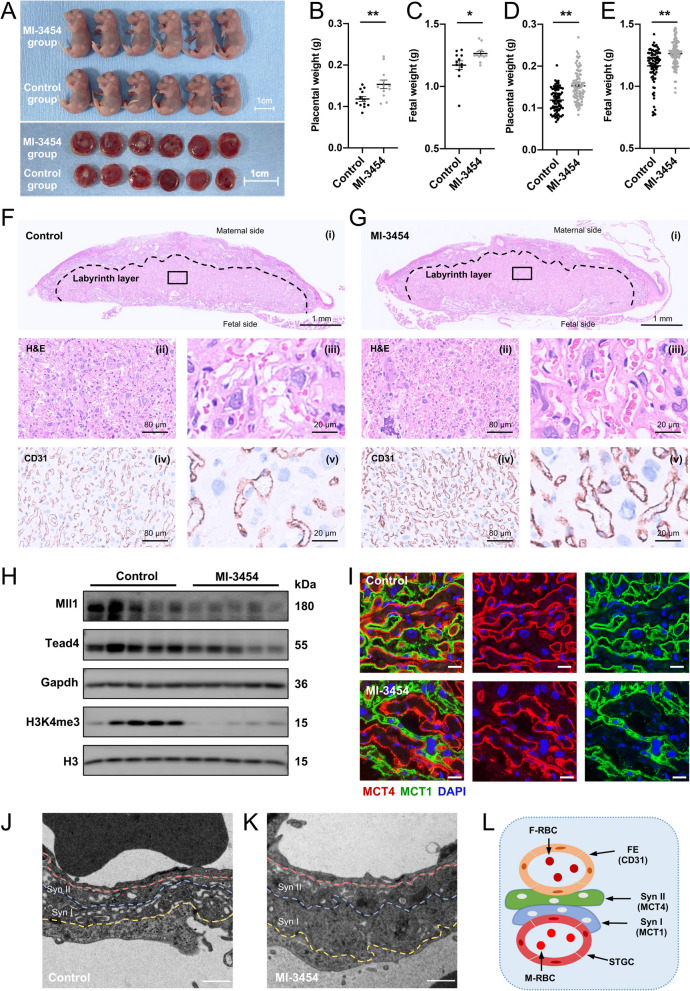
Fig. 8.
Effect of intraperitoneal administration of MI-3454 on fetoplacental weights in mice. A Representative appearance of the MI-3454 and control fetuses and placentas. B-E Administration of inhibitor MI-3454 (15 mg/kg boy weight (BW)) increased the average fetal and placental weights both litters (Control group, n = 12; MI-3454 group, n = 12) (B and C) or in fetuses (Control group, n = 87; MI-3454 group, n = 88) (D and E). F and G H&E staining (i-iii) and immunostaining against CD31 (iv and v) of the control (n = 6) (F) and MI-3454 (n = 6) (G) placentas at E18.5. Panels (iii) and (v) in F and G are the corresponding higher magnification images of panels (ii) and (iv), respectively. (H) Western blots of Mll1, Tead4, and H3K4me3 in the control (n = 5) (F) and the MI-3454 (n = 5) (G) placentas at E18.5. (I) Immunofluorescent staining of MCT1 (green), MCT4 (red), and DAPI (blue) in the indicated placentas (n = 5). Scale bar, 20 μm. (J and K) Representative transmission electron microscopy images of STBs in mouse placentas treated with vehicle (n = 3) (J) or MI-3454 (n = 3) (K). Scale bar, 1 μm. L Schematic depiction of the mouse placenta. MCT1 specifically expresses in the SynT-1 layer, while MCT4 specifically stains the SynT-2 layer. Data are presented as the means ± SD. **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05. FE, fetal endothelium; F-RBC, fetal red blood cell; M-RBC, maternal red blood cell; STGC, sinusoidal trophoblast giant cell; Syn I, the first layer of STBs; Syn II, the second layer of STBs; H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; CD31, platelet and endothelial cell adhesion molecule 1; MCT1, monocarboxylate transporter 1; MCT4, monocarboxylate transporter 4