Figure 2.
The SNCA risk enhancer shows evidence of functionality via 3D chromatin interactions and transcription factor binding
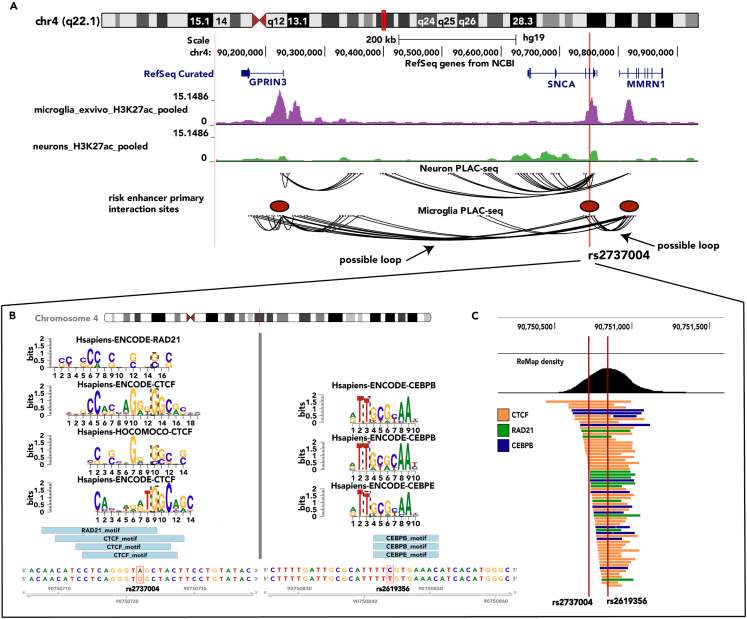
(A) H3K27ac ChIP-seq tracks are displayed for microglia (purple) and neurons (green). Below are tracks showing PLAC-seq data for the same cell types. The red ovals denote primary interaction sites, in microglia, of the risk enhancer where rs2727004 is located.
(B) MotifbreakR results showing transcription factor (TF) binding motifs of the TFs that have preference for the alleles of the risk haplotype (G for rs2737004 (left) and T for rs2619356 (right)). The letter size represents the results of the positional weight matrix that measures the frequency that the transcription factor binds to that nucleotide. In that same plot, the dashed black box demarcates the position of the SNP. The light blue boxes below represent the positions of the transcription factor binding motifs relative to the SNP’s genomic position, demarcated with the red box.
(C) Remap ChIP-seq data for the transcription factors displayed in part B. The red lines show the position of each SNP within the ChIP-seq peak.