Fig. 1. Mutational Analysis of individuals with arRP due to EYS mutations.
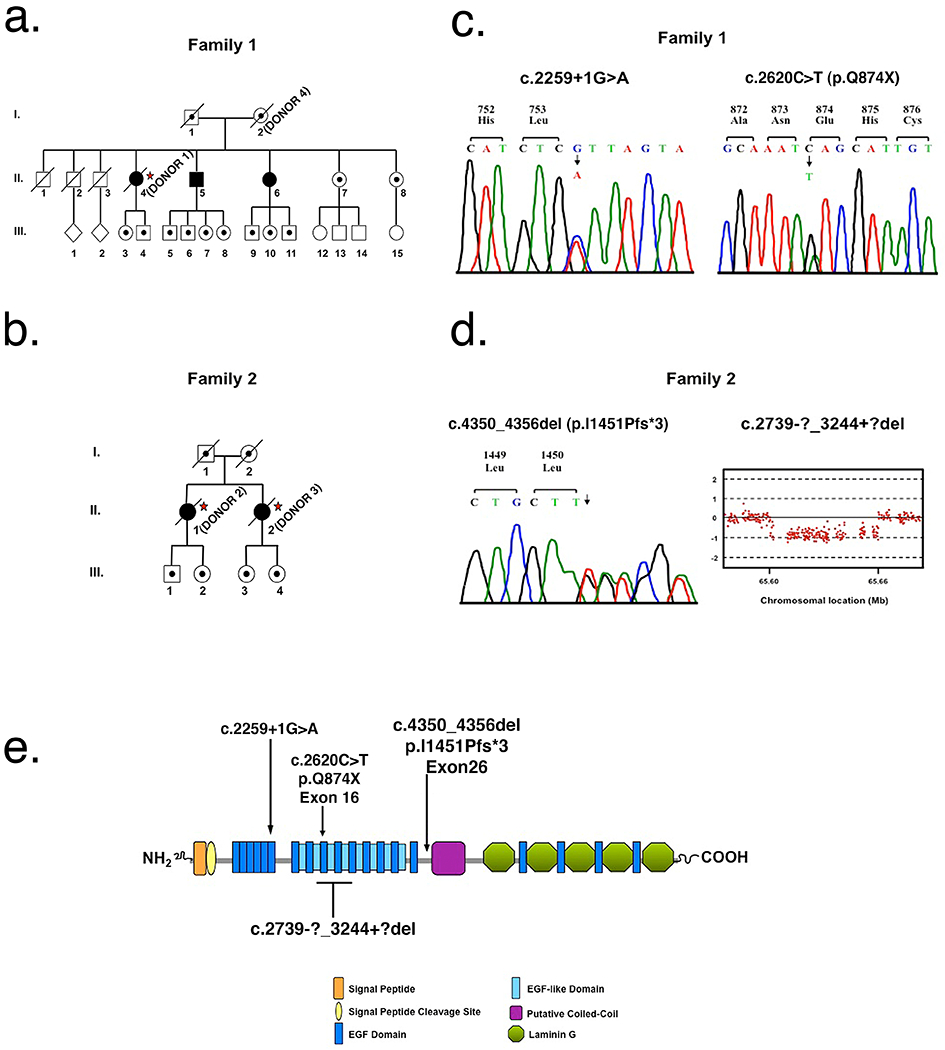
a Pedigree of family 1. Slashed symbols reflect deceased family members. Affected family members are shown with filled symbols, unaffected family members are shown with unfilled symbols and unaffected carrier family members are shown with unfilled symbols with a black dot inside. Postmortem analysis was done on affected member II-4 referred to as donor 1 (*) and in their unaffected mother (I-2) referred to as donor 4 (*). b Pedigree of family 2. Postmortem analysis was done on affected members II-1 and II-2 referred to as donors 2 (*) and 3 (*), respectively. c Sequence analysis of family 1 identified two heterozygous EYS mutations, c.2259+1G>A and p.Q874X. DNA analysis was performed on all three affected members (II-4, II-5 and II-6), their two unaffected living sisters (II-7 and II-8), and their mother (I-2). d Sequence analysis of family 2 identified a heterozygous 7 base pair deletion in EYS, p.I1451Pfs*3. Comparative genomic hybridization identified a heterozygous deletion of exons 15 – 18, c.2739-?_3244+?del. DNA analysis was performed in two affected family members, II-1 and II-2. e Predicted domain structure and distribution of the four EYS mutations identified in this study.
