Fig. 5. Immunocytochemistry of arRP retinal sections with EYS mutations stained with rhodopsin antibodies.
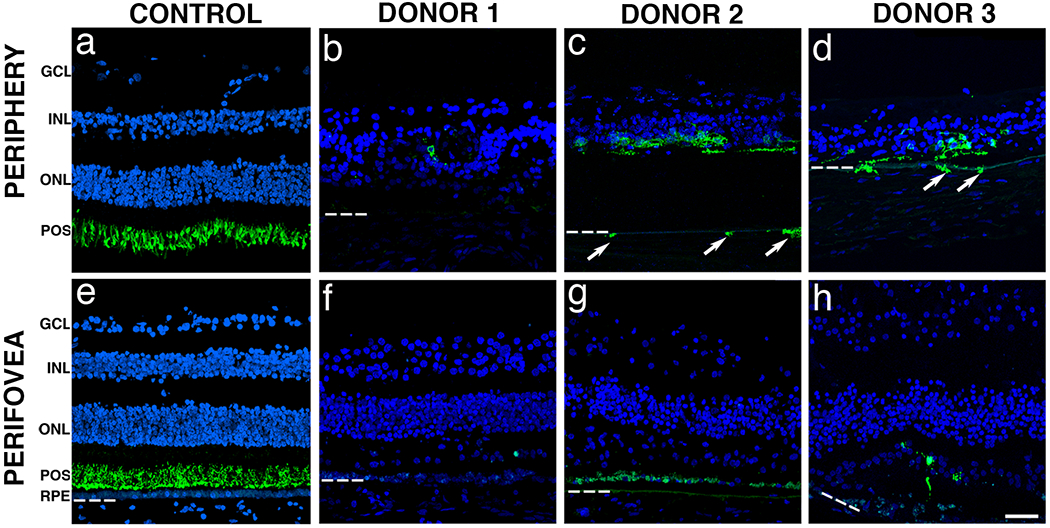
Immunofluorescence of arRP retinal sections labeled with antibodies to rhodopsin (green) showed significantly decreased staining when compared to control. The control retina showed that rhodopsin was restricted to the rod outer segments in both the periphery (a) and perifovea (e). Rhodopsin-labeled cells were essentially absent from the periphery of donor 1 (e). However, rhodopsin-labeled cells were still present in the periphery of donors 2 (c) and 3 (d). Of interest, some rhodopsin-labeled cells were observed in the choroid of these eyes (arrows). In the perifovea, donors 1 (f) and 2 (g) displayed no rods while donor 3 (h) displayed a few disorganized rods. Bruch’s membrane is indicated by hashed white line. Nuclei were labeled with TO-PRO-3. GCL= ganglion cell layer; INL= inner nuclear layer; ONL= outer nuclear layer; POS = photoreceptor outer segments; RPE= retinal pigment epithelium. Scale bar = 40μm.
