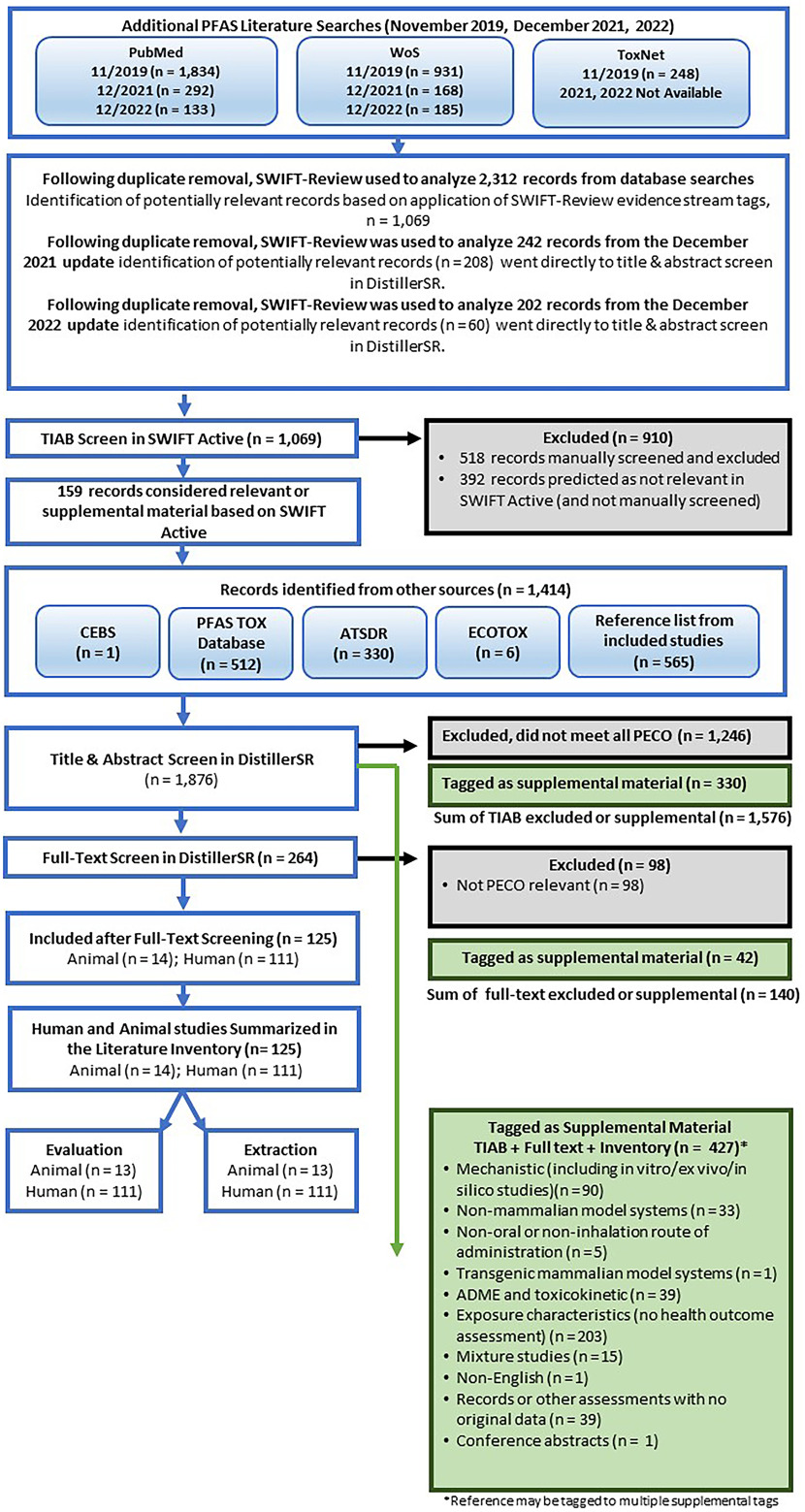
Figure 4.
Additional PFAS study flow diagram (3 November 2023). Literature Searches and results are pooled across years. References identified from other sources joined screening at Distiller SR title-abstract review. Some references may have multiple supplemental or exclusion tags. Note: ADME, absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion; ATSDR, Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry; CEBS, National Toxicology Program Chemical Effects in Biological Systems; ECOTOX, US EPA Ecotoxicology Knowledgebase; HAWC, Health Assessment Workspace Collaborative; PBPK, physiologically-based pharmacokinetic; PECO, populations, exposure, comparator, outcome criteria; PFAS, per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances; PFAS Tox Database, 2019 PFAS evidence map42,45,46; TIAB, title and abstract screening; WoS, Web of Science.