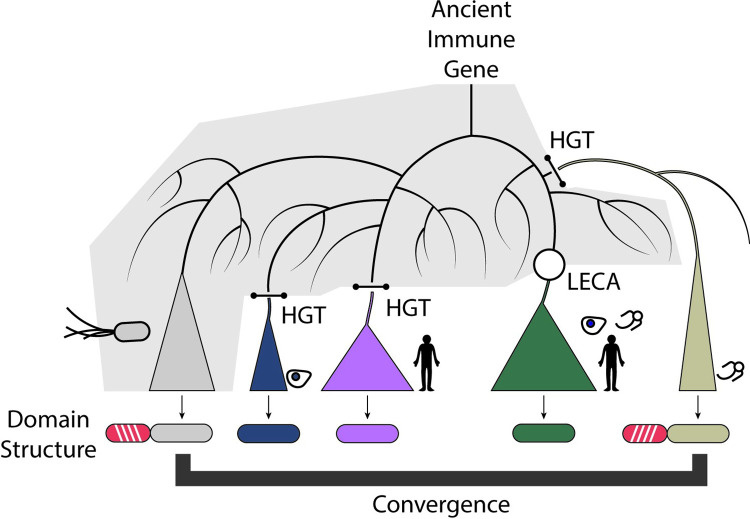
Fig 1. Evolutionary routes connecting ancient immune genes to modern eukaryotic genomes.
Illustration of evolutionary mechanisms enabling eukaryotic acquisition of innate immune machinery from bacteria. Gray background illustrates bacterial sequences, with transition to white background indicating inheritance by eukaryotes. Through analysis of the evolutionary history of CD-NTase, STING, and viperin proteins, Culbertson and Levin highlight 3 broad mechanisms of eukaryotic immune gene evolution: vertical inheritance from LECA (green clade), horizontal gene transfer to specific eukaryotic clades groups (blue, pink, and tan clades), and convergent domain shuffling where similar accessory domains (red with white hashes) are found fused to the same immune gene (tan clade). CD-NTase, cGAS/DncV-like nucleotidyltransferase; HGT, horizontal gene transfer; LECA, last eukaryotic common ancestor; STING, stimulator of interferon genes.