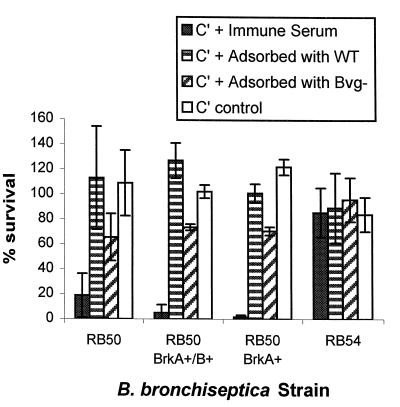
FIG. 2.
Serum susceptibility of B. bronchiseptica strains. Percent survival was calculated for bacteria incubated in serum. ▪, 50% heat-inactivated immune serum as a source of antibodies (Colorado serum no. 421) plus 50% complement (C′), Sigma guinea pig serum;  , 50% heat-inactivated immune serum preadsorbed with RB50 (serum adsorbed with wild type [WT]) to remove surface antibodies plus 50% complement;
, 50% heat-inactivated immune serum preadsorbed with RB50 (serum adsorbed with wild type [WT]) to remove surface antibodies plus 50% complement;  , 50% heat-inactivated immune serum preadsorbed with RB54 (serum adsorbed with Bvg−) to remove surface antibodies plus 50% complement; □, PBS plus 50% complement. Results from four experiments were averaged. RB50, RB50 BrkA+ BrkB+ (containing plasmid pUW2171), and RB50 BrkA+ (containing plasmid pRF1009) were significantly more sensitive to heat-inactivated serum with complement than complement alone or complement plus serum adsorbed with RB50 (P < 0.02 to 0.04). In addition, RB50 incubated with heat-inactivated serum plus complement was significantly more sensitive than RB54 incubated with heat-inactivated serum plus complement (P < 0.01). The error bars indicate standard deviations. The data were analyzed by the paired t test.
, 50% heat-inactivated immune serum preadsorbed with RB54 (serum adsorbed with Bvg−) to remove surface antibodies plus 50% complement; □, PBS plus 50% complement. Results from four experiments were averaged. RB50, RB50 BrkA+ BrkB+ (containing plasmid pUW2171), and RB50 BrkA+ (containing plasmid pRF1009) were significantly more sensitive to heat-inactivated serum with complement than complement alone or complement plus serum adsorbed with RB50 (P < 0.02 to 0.04). In addition, RB50 incubated with heat-inactivated serum plus complement was significantly more sensitive than RB54 incubated with heat-inactivated serum plus complement (P < 0.01). The error bars indicate standard deviations. The data were analyzed by the paired t test.