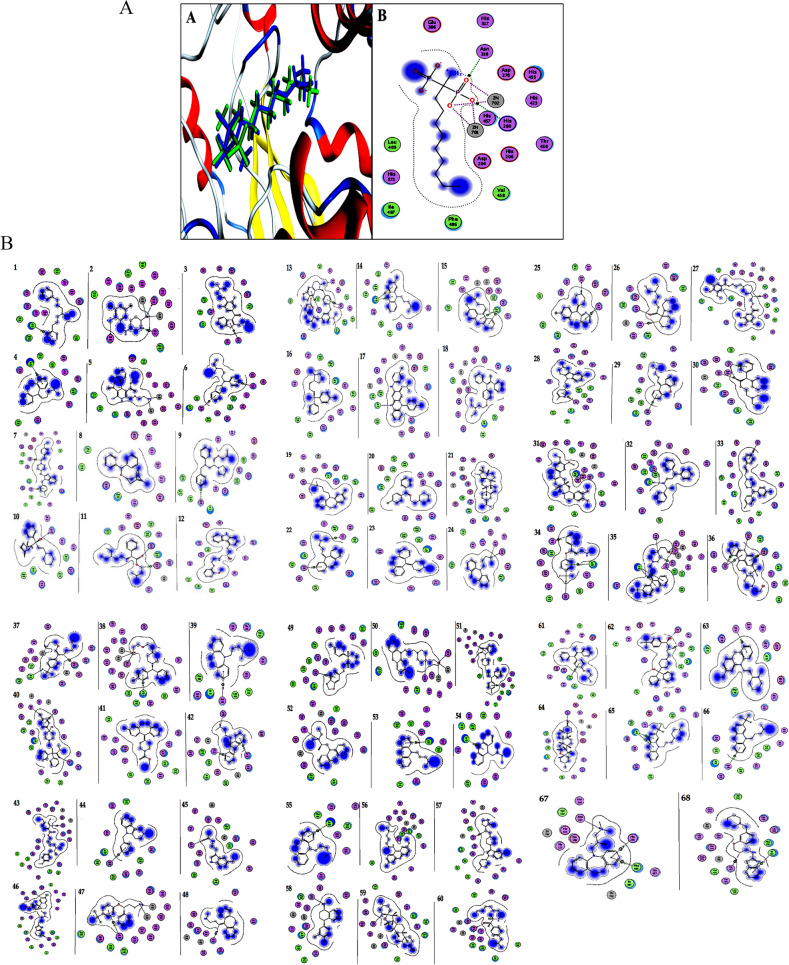
Fig. 7.
A (i) Superimposition of the docking pose (green) and the co-crystallized (blue) of (1-azanyl-1-phosphono-decyl) phosphonic acid (APPA) in the acid sphingomyelinase active site with RMSD of 1.49 Å. (ii) 2D interaction diagram showing APPA docking pose interactions with the hot spots in the enzyme active site. B. 2D diagrams of the candidate drug (amiodarone) and the reported inhibitors. 1. Alverine, 2. Ambroxol, 3. Amiodarone, 4. Amitriptyline, 5. Amlodipine, 6. Aprindine, 7. Astemizole,8.Benztropine, 9. Bepridil, 10. Biperidene, 11. Camylofine, 12. Carvedilol, 13. Cepharanthine, 14. Chlorpromazine, 15. Chlorprothixene, 16. Clemastine, 17. Clofazimine, 18. Clomiphene, 19. Clomipramine, 20. Cloperastine, 21. Conessine, 22. Cyclobenzaprine, 23. Cyproheptadine, 24. Desipramine, 25. Desloratadine, 26. Dicycloverine, 27. Dilazep, 28. Dimebon, 29. Doxepine, 30. Drofenine, 31. Emetine, 32. Fendeline, 33. Flunarizine, 34. Fluoxetine, 35. Flupenthixol, 36. Fluphenazine, 37. Fluvoxamine, 38. Hydroxyzin, 39. Imipramine, 40. Loperamide, 41. Loratadine, 42. Maproteline, 43. Mebeverine, 44. Mebhydrolin, 45. Melatonin, 46. Mibefradil, 47. Norfluoxetine, 48. Nortriptyline, 49. Paroxetine, 50. Perphenazine, 51. Pimozide, 52. Profenamine, 53. Promazine, 54. Promethazine, 55. Protriptyline, 56. Quinacrine, 57.Sertindole, 58. Sertraline, 59. Solasodine, 60. Suloctidil, 61. Tamoxifene, 62. Terfenadine, 63. Thioridazine, 64. Tomatidine, 65. Trifluoperazine, 66. Triflupromazine, 67. Trimipramine, 68. Zolantidine showing their interaction with the key amino acids in the acid sphingomyelinase