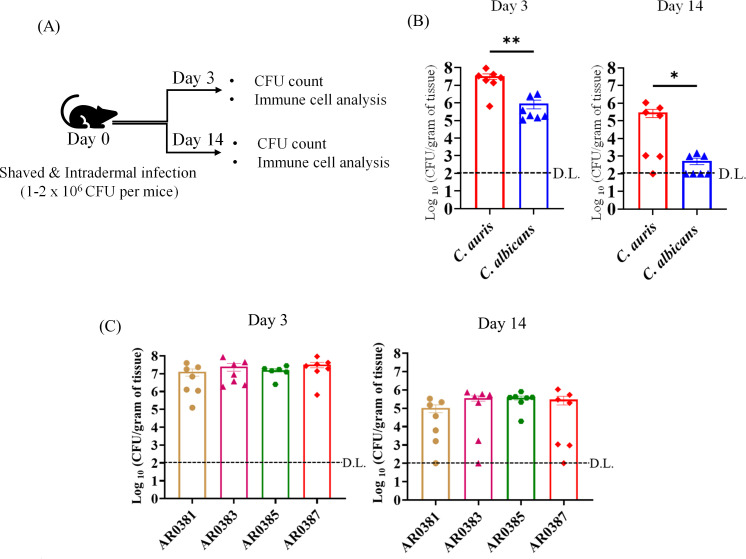
Fig 1.
(A) Schematic of experimental design shown here. Mice were shaved and injected with PBS (or) infected intradermally with fungal cells on day 0. Fungal load in the skin of mice and immune cell isolation and analysis were determined on day 3 and day 14 post-infection. (B) Fungal load in the skin tissue of mice intradermally infected with C. auris AR0387 (or) C. albicans SC5314 after 3 and 14 days post-infection is shown here. (C) Fungal load in the skin tissue of mice intradermally infected with C. auris AR0381, C. auris AR0383, C. auris AR0385, or C. auris AR0387 after 3 and 14 days post-infection is shown here. Fungal load was determined by plating the homogenized skin tissue onto YPD agar containing the following antibiotics: ampicillin, streptomycin, and kanamycin. C. auris or C. albicans colonies were further confirmed by plating the homogenates onto CHROMagar plates. For days 3 and 14, each symbol represents the fungal load from each mouse (n = 6–7 per group). Data are represented as mean ± standard error of the mean for each group. Statistical significance was calculated using Mann-Whitney U test or the Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. *P ≤ 0.05 and **P ≤ 0.01 were considered as significant. D.L., detectable limit of fungal colonies.