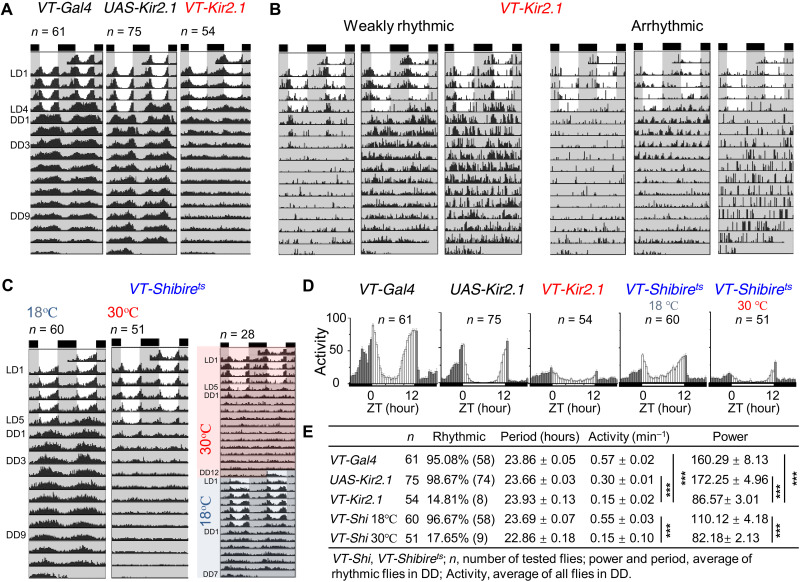
Fig. 7. xCEOs sustain free-running behavioral locomotor rhythms.
(A) Actograms of VT037867-Gal4 (left), UAS-Kir2.1 (middle), and VT037867-Kir2.1 flies (right). (B) Representative weak rhythmicity (left) and arrhythmicity (right) in VT037867-Kir2.1 flies. (C) VT037867-Shibirets flies maintained free-running rhythms at 18°C (left) but lost free-running rhythms at 30°C (middle) and the lost free-running rhythms at 30°C recovered at 18°C (right). (D) Activity histograms of VT037867-Gal4, UAS-Kir2.1, VT037867-Kir2.1, and VT037867-Shibirets flies in LD. (E) DD rhythmicity statistics (period, activity, and power) of VT037867-Gal4, UAS-Kir2.1, VT037867-Kir2.1, and VT037867-Shibirets flies. For activity, ***P(VT037867-Gal4/VT037867-Kir2.1) < 0.001, ***P(UAS-Kir2.1/VT037867-Kir2.1) < 0.001, and ***P(18°C/30°C) < 0.001 for VT037867-Shibirets flies; for power, ***P(VT037867-Gal4/VT037867-Kir2.1) < 0.001, ***P(UAS-Kir2.1/VT037867-Kir2.1) < 0.001, and ***P(18°C/30°C) < 0.001 for VT037867-Shibirets flies. These data are analyzed by Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA with Dunn’s test. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. Actograms and histograms are averaged from four independent replicates.