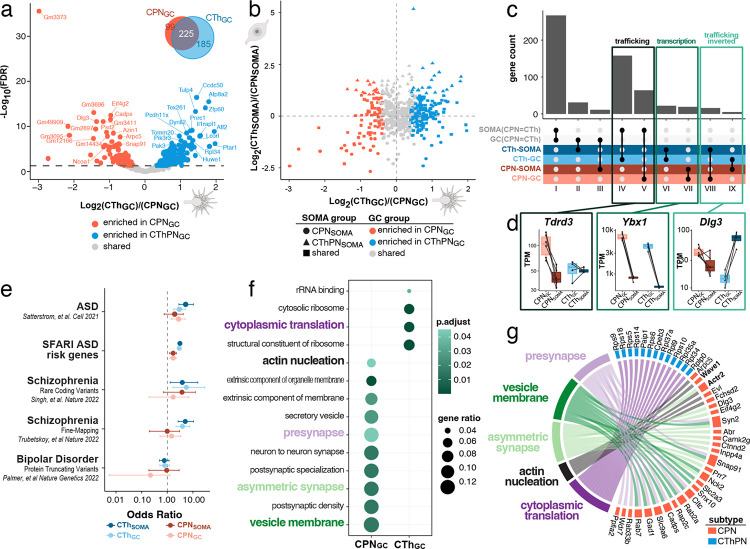
Figure 2: Distinct subtype-specific, GC-specific, local transcriptomes of CPN and CThPN are enriched with potential regulators of distinct axon guidance decisions.
(a) Volcano plot indicating subtype-specific, GC-localized transcripts as colored dots (FDR. < 0.05). Venn diagram shows distribution of shared and distinct GC-specific molecular machinery between subtypes. (b) Transcriptomic differences between CPN and CThPN across subcellular compartments (somata vs. GCs). (c) Comparison of subtype-specific, GC-localized transcriptomes reveals molecular machinery that is shared between CPN and CThPN (classes I-III) and distinct between subtypes (IV-IX). Importantly, differences between GCs of distinct subtype are often not captured by comparing subtype-specific somata alone; we denote these as “trafficking” distinctions between subtypes (classes IV, V, VIII, IX), as opposed to those driven by “transcription” (classes VI, VII). (d) Normalized transcript abundances of exemplar genes for classes IV/V (“trafficking”, Tdrd3), classes VI/VII (“transcription”, Ybx1), and classes VIII/IX (“trafficking inverted”, Dlg3), across subcellular compartments and subtypes. (e) ASD and schizophrenia disease-associated genes are enriched (95% confidence interval) in soma- and GC-enriched transcriptomes. Both CPN and CThPN soma-localized and GC- localized transcriptomes show enrichment for ASD-associated genes, based on comparison with two independent data sets. Cross-referencing with two independent GWAS studies for schizophrenia additionally revealed that CThPN soma- and GC-localized transcriptomes are also enriched for schizophrenia-associated genes. There is no enrichment detected with genes associated with bipolar disorder in either CPN or CThPN transcriptomes, serving as a neuropsychiatric disease control, highlighting specificity in ASD and schizophrenia. (f) GO term enrichment in the GC-localized, subtype-distinct genes of each subtype. Color indicates −log10(P-value). (g) Subset of GO terms significantly enriched in either CPN or CThPN GCs connected with genes in GCs that are most frequently represented by those GO terms. Color of block proximal to each gene name denotes its subtype enrichment at P3. Bolded genes are core components/interactors of the WRC (Fig. 3).