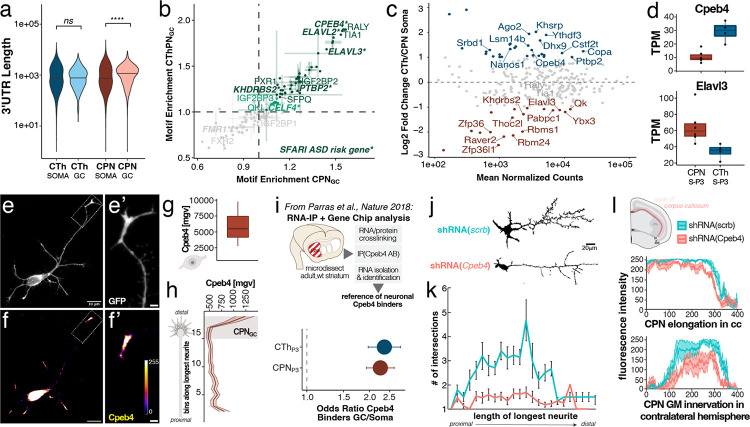
Figure 4: GC-localized mRNAs of both subtypes exhibit shared 3’UTR and motif characteristics, and are enriched for motifs associated with CPEB4.
(a) 3’UTRs are on average longer in GCs than in somata. (b) Motif enrichment in GCs vs. somata is highly correlated between CPN and CThPN GCs; the most GC-enriched poly-U motifs are associated with CPEB4, RALY, and TIA1. (c) Comparison of CPN and CThPN soma-localized RNA expression of RBPs, annotated by GO term 0003729. Subtype-specific RBPs are highlighted in red (CPN) and blue (CThPN), FDR < 0.05 and fold change > 2. (d) RNA expression in CPN (red) and CThPN somata (blue) for Cpeb4 and Elavl4. (e & f) Cultured mouse CPN expressing myristoylated GFP, with distal axon (longest neurite) magnified in (e’); immunolabeling for CPEB4 is shown in (f) with magnification showing distal axon enrichment of CPEB4 in (f’). (g) Quantification of mean gray value of Cpeb4 immunolabeling in somata of primary cultured CPN (n = 6). (h) Analysis of same gray value scale of CPEB4 immunolabeling intensity binned from proximal axon (bottom) to distal GC (top) for the longest neurite (n = 6). (i) CPEB4-bound mRNAs identified by RIP-seq2 are highly enriched in GCs of both subtypes as compared to their somata. (j) Cultured CPN fixed at 3 days in vitro (DIV3) display decreased axon branching complexity following Cpeb4 shRNA-mediated knockdown. (k) Sholl analysis of branching complexity of longest neurite of cultured CPN, comparing neurons treated with Cpeb4 shRNA (n = 15) or scrambled control shRNA (n = 15). Intersections (mean ± sem) with concentric spheres spaced every 10 μm around the cell body are quantified. (l) Constitutive shRNA knockdown of Cpeb4 in CPN (red, n = 3) by in utero electroporation does not nonspecifically affect axons elongating into the corpus callosum, but it significantly reduces innervation of the contralateral gray matter compared to CPN treated with a scrambled shRNA control (scrb, teal, n = 4).