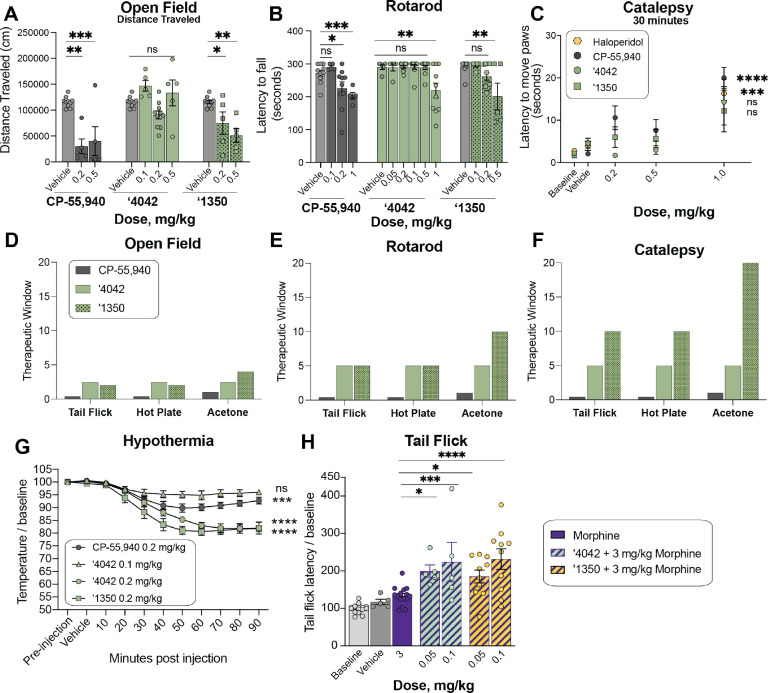
Figure 6. In vivo side-effect and cotreatment profile of ‘4042 and ‘1350.
A. Dose-response of ‘1350 (all n = 5; one-way ANOVA, F(2, 17) = 9.5, P = 0.002), ‘4042 (0.1 and 0.5 mg/kg, n = 5; 0.2 mg/kg n = 10; one-way ANOVA, F(3, 26) = 5.3, P = 0.006) and CP-55,940 (all n = 5; one-way ANOVA, F(2, 17) = 13.7, P < 0.001) in the open-field test of hypolocomotion. Asterisks define individual group differences to vehicle control after Dunnett’s multiple comparisons post-hoc test correction. B. Rotarod test of sedation comparison of CP-55,940 (all n = 5 except 0.2 mg/kg n = 10; one-way ANOVA, F(3, 26) = 5.7, P = 0.04) to ‘4042 (all n = 10 except 0.05 mg/kg n = 5; one-way ANOVA, F(5, 44) = 6.2, P < 0.001) and ‘1350 (all n = 5 except 0.2 mg/kg n = 10; one-way ANOVA, F(3, 26) = 5.7, P = 0.004); asterisks define individual group differences to respective vehicle control after Dunnett’s multiple comparisons post-hoc test correction. C. Mesh grip test of catalepsy at 30 minutes post-dose. Comparison of CP-55,940 (n = 5–10; one-way ANOVA, F(3, 26) = 10.7, P < 0.0001), haloperidol (n = 5; two-tailed unpaired t-test, t(8) =6.2, P < 0.001), ‘4042 (n = 5; one-way ANOVA, F(3, 16) = 4.1, P = 0.02) and ‘1350 (n = 5–10; one-way ANOVA, F(3, 26) = 1.02, P = 0.4). Asterisks define differences between 1 mg/kg dose for each compound and respective vehicle control. Data at 1 hr timepoint are in Fig. S11. D-F. Therapeutic windows for each analgesia test versus hypolocomotion (D., open field), sedation (E., rotarod), and catalepsy (F.) side-effects. Therapeutic window was calculated as the ratio of the minimum dose of side-effect onset or maximum tested side-effect dose if no doses were significant to the minimum dose of analgesia onset. G. Body temperatures of mice treated with CP-55,940 (n = 5; one-way ANOVA, F(10, 44) = 13.3, P < 0.0001), ‘4042 (0.1 mg/kg; n = 5; one-way ANOVA, F(10, 44) = 3.5, P = 0.002; 0.2 mg/kg; n = 5; one-way ANOVA, F(10, 44) = 32.2, P < 0.0001) and ‘1350 (n = 3; one-way ANOVA, F(10, 22) = 27.3, P < 0.0001). Asterisks define differences between each group at 90 min. post-dose and their respective vehicle control. mg/kg dose for each compound and respective vehicle control. H. Cotreatment of subthreshold dose of morphine with ‘4042 (one-way ANOVA, F(4, 40) = 11.0, P < 0.0001) and ‘1350 (one-way ANOVA, F(4, 50) = 14.7, P < 0.0001) in the tail flick test. Asterisks define cotreatment differences to morphine alone (3 mg/kg) using Dunnett’s multiple comparisons post-hoc test correction. For all statistical tests: ns, not significant, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.