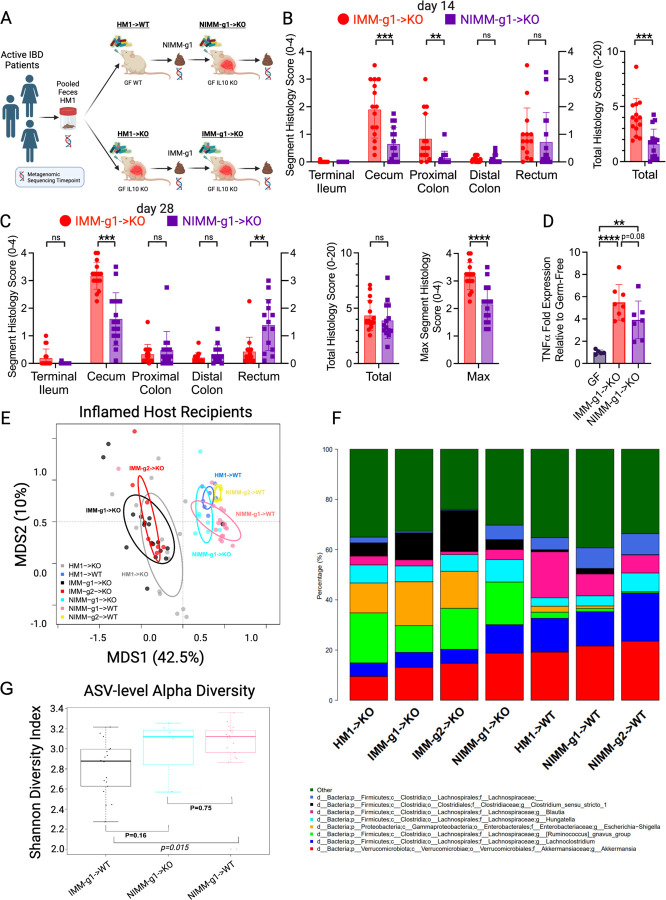
Figure 6. Inflamed mouse-adapted microbiome more rapidly induces severe colitis than non-inflamed mouse adapted microbiome.
A). Experimental design. Human IBD patient microbiota (HM1) was adapted in the inflamed (IMM-g1) or non-inflamed (NIMM-g1) host, then transplanted to Il-10−/− (KO) GF recipient mice. B) Segment and total colon + ileum histology score for KO mice at day 14 post-colonization. C) Segment, total colon + ileum, and max segment histology score for KO mice at day 28 post-colonization. D) TNFα mRNA levels in cecal tissue at day 28 post-colonization. E) PCoA of FMT recipient WT and KO mouse groups, including NIMM-g1->KO group. F) 16S Seq taxonomic barplots show top 8 most abundant genera in FMT inputs and recipient mouse feces at day 28 post-colonization. For mouse recipient groups, barplots are average of 16S seq data from n=7–18 mice/group. G) Shannon diversity index at ASV level for IMM-g1->WT, NIMM-g1->KO and NIMM-g1->WT groups. Data shown are representative of (D) or cumulative (B-C, E-F) from 2–4 independent experiments. n=15–16 (B-C), n=5–8 (D), n=7–16 (E-G) mice per group. Data are expressed as mean±SD. Statistical significance calculated by unpaired t-test (B-D, G) with *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.