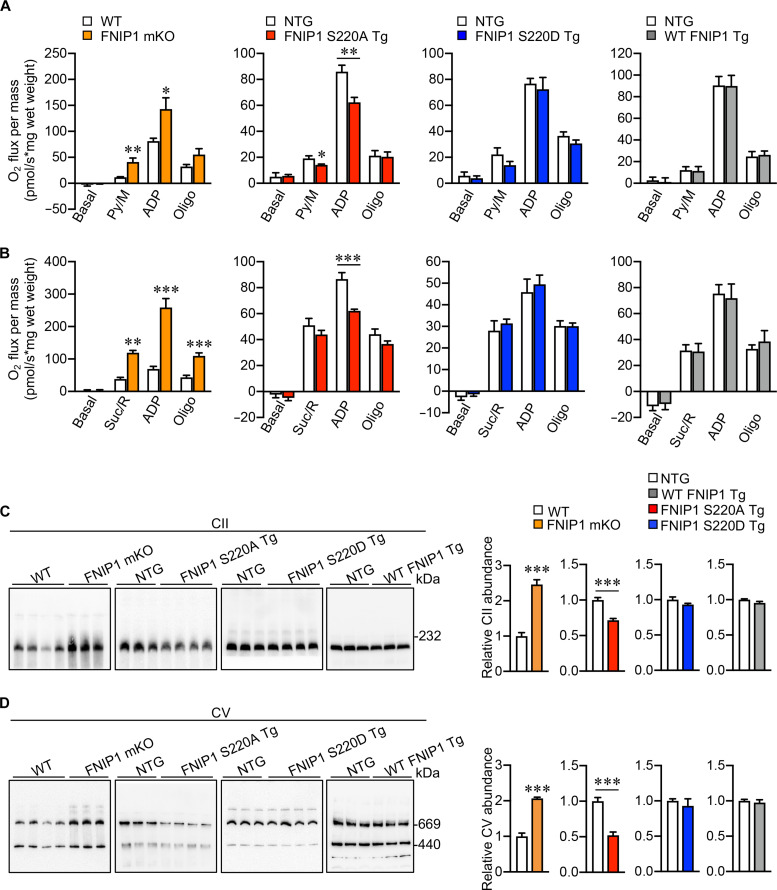
Fig. 5. FNIP1 (S220) phosphorylation regulates mitochondrial ETC complex formation and respiration capability in muscle.
(A and B) Mitochondrial respiration rate analysis in FNIP1 mKO and transgenic (Tg) muscle tissues. Mitochondrial respiration rates were determined from the extensor digital longus (EDL) muscle of the indicated genotypes using pyruvate (A) or succinate (B) as substrates. Pyruvate/malate (Py/M)– or succinate/rotenone (Suc/Rot)–stimulated, adenosine diphosphate (ADP)–dependent respiration, and oligomycin-induced (Oligo) respiration are shown. n = 4 to 7 mice per group. (C and D) The effects of FNIP1 (S220) phosphorylation on mitochondrial ETC complex assembly in the muscle. Mitochondrial proteins were extracted from the indicated mice after exercise and analyzed by BN-PAGE as described in Materials and Methods. Western blotting analysis was performed with anti-SDHA (CII) (C) and anti-ATP5A (CV) (D) antibodies. Equal total mitochondrial proteins were loaded, and the band gray values were quantified using ImageJ. WT and FNIP1 mKO mice, exercise for 150 min; NTG and Fnip1 Tg mice, exercise for 60 min. n = 3 to 8 mice per group. Error bars are shown as the means ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. The P value was determined by Student’s t test.