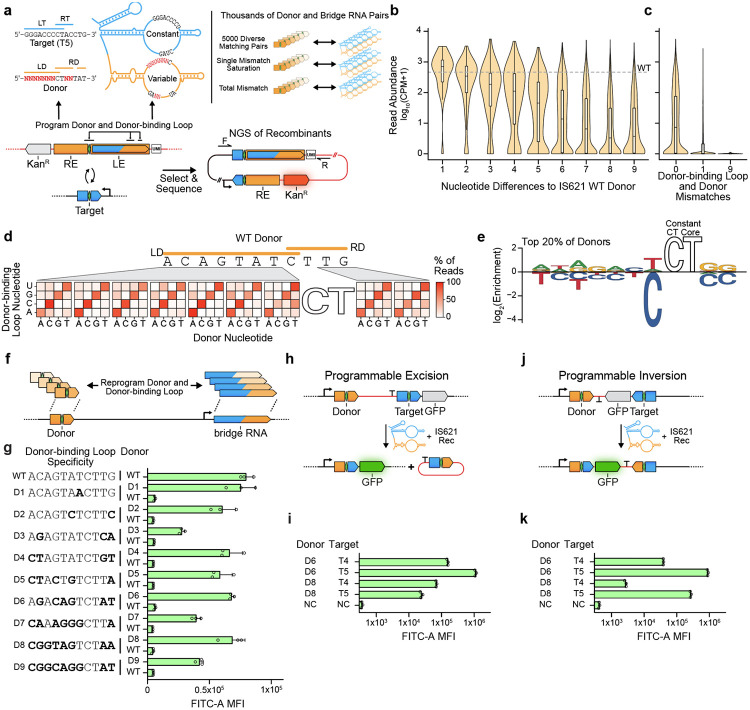
Figure 5: Bridge RNA donor recoding enables fully programmable insertion, inversion, and excision.
(a) Schematic representation of the high throughput donor screen. The recombination assay design uses the same approach as in Fig. 3a and 3c, except that the expression of a kanamycin resistance gene is induced and surviving colonies are assayed. A unique molecular identifier (UMI) identifies each pair of donor and donor-binding loops. The bridge RNA target-binding loop is matched to target T5. Two replicates were averaged to produce read abundance per oligo, quantified as CPM, counts per million. NGS, next generation sequencing.
(b) Reprogrammability of donor sequences by number of nt differences from the WT donor. Wild-type donor abundance is indicated by the gray dashed line. CPM, counts per million.
(c) Mismatch tolerance between non-core sequences of the donor-binding loop and donor. CPM, counts per million.
(d) Mismatch tolerance between bridge RNA donor-binding loop and donor by position. The percentage of total detected recombinants encoding each single mismatch is recorded. The core of the donor and core-binding sequences of the donor-binding loop are constant across displayed recombinants.
(e) Nucleotide enrichment of efficient perfectly matched pairs of donors and donor-binding loops. Sequence logo represents the nucleotide enrichment at each position among the top 20% most efficient targets tested in the donor specificity screen.
(f) Schematic illustrating paired reprogramming of donor/donor-binding loop. donor-binding loops were reprogrammed and tested against the wild-type donor and their cognate donor.
(g) Specific recombination using reprogrammed donor and bridge RNA donor-binding loop sequences. Donor sequences are listed at left, and the bridge RNA is reprogrammed to base-pair with the indicated sequence. Bold bases highlight differences relative to WT donor sequence. MFI ± SD for three biological replicates shown.
(h) Schematic representation of the programmable excision assay.
(i) Efficient programmable excision of DNA. Pairs of donor and target are denoted. Negative control (NC) expresses the reporter and recombinase but no bridge RNA. MFI ± SD for three biological replicates shown.
(j) Schematic representation of the programmable inversion recombination assay.
(k) Efficient programmable inversion of DNA. Pairs of donor and target are denoted. Negative control (NC) expresses the reporter and recombinase but no bridge RNA. MFI ± SD for three biological replicates shown.