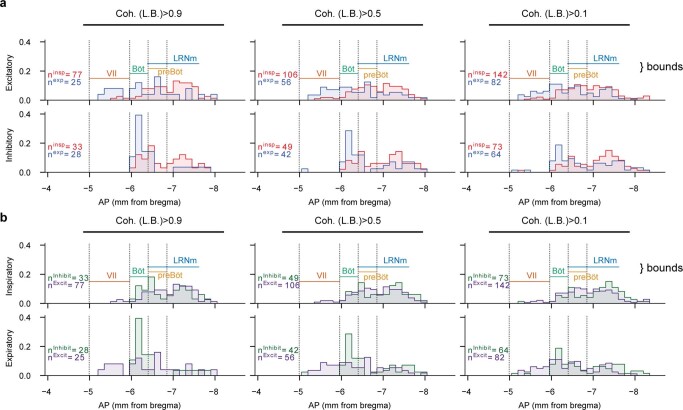
Extended Data Fig. 2. Anterior-posterior distributions of somatic units of identified genotype and respiratory activity pattern.
Given that Dbx1+ neurons are glutamatergic, we combine Dbx1+ opto-tagged neurons with Vglut2+ opto-tagged neurons to identify the excitatory units. (a) AP distributions of inspiratory (red) and expiratory (blue) units that are excitatory (top) or inhibitory (bottom) for varying coherence thresholds (left to right). Y-axis is probability of a unit being in a given bin (150 μm), normalized within the identified group (that is, inspiratory or expiratory are normalized independently). Of note is the high proportion of inhibitory neurons in the canonical Bötzinger complex, particularly if analyses are restricted only to strongly coherent neurons, and the high proportion of inspiratory neurons caudal to the preBötC, likely including bulbospinal rVRG premotor populations. AP extent of landmark regions in the ventral medulla are shown, but histograms include units from all regions that overlap at a given AP location (b) Same data as in (a), but colored by excitatory (purple)/inhibitory (green); inspiratory neurons in top row, expiratory neurons in bottom.