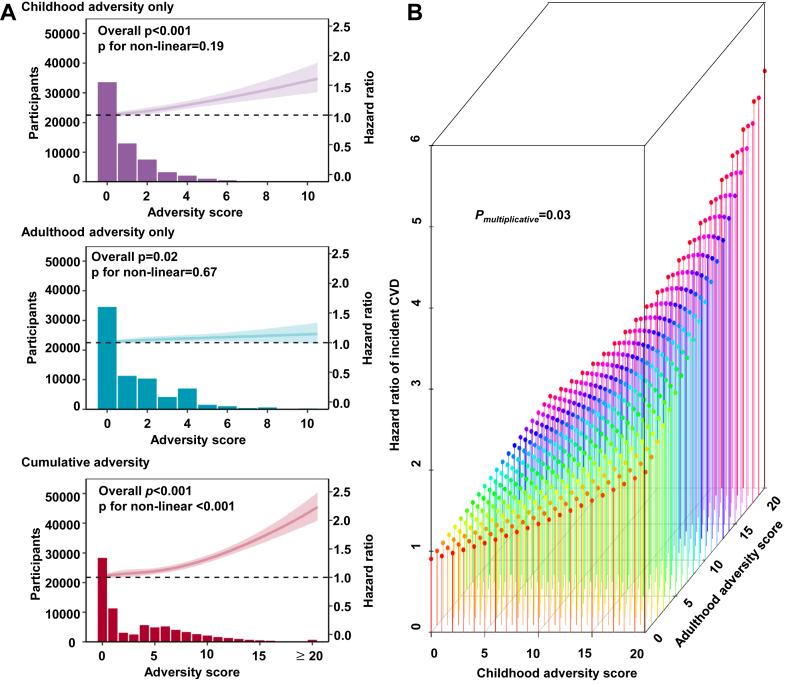
Fig. 3.
Interactions between childhood and adulthood adversities on the risk of CVD among 136,073 participants in the UKB. (A) Cox proportional regression models with restricted cubic spline terms for adversity score were used to examine the associations between the scores and risk of CVD, with adjustment for age, sex, race/ethnicity, Townsend deprivation index, and family history of heart diseases and stroke. (B) Interaction surface plot on the linear predictor of the hazard function. The z-axis shows the predictor of the hazard function for varying scores of childhood adversities and adulthood adversities, illustrating their interacting effect on the risk of CVD. Cumulative adversities denote adversities in both childhood and adulthood.