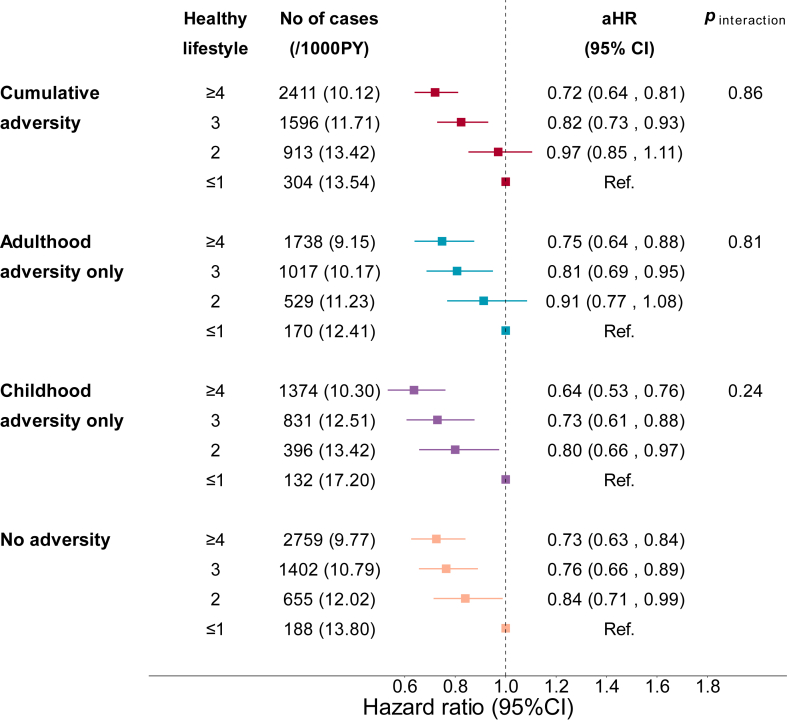
Fig. 4.
Risk of CVD according to adversities and number of ideal lifestyle factors among 136,073 participants in the UKB. Ideal lifestyle factors were defined as follows: no smoking, regular physical activity (≥150 min/week of moderate activity or ≥75 min/week of vigorous activity), a healthy diet (including at least 5 healthy foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, (shell)fish, dairy, vegetable oils, and fewer refined grains, processed meats, unprocessed meats, and sugar-sweetened beverages), adequate sleep (7–9 h per day), engagement in social or leisure activities (like sports clubs or gyms, pubs or social clubs, religious groups, adult education classes, and other group activities), and participating in friend or family visits at least once a week. The Cox proportional hazard model was used for the analysis, with adjustment of age, sex, race/ethnicity, Townsend deprivation index, and family history of heart diseases and stroke. p values for interaction were calculated by including the product term of adversity and lifestyle in model. Cumulative adversities denote adversities in both childhood and adulthood.