Fig. 2.
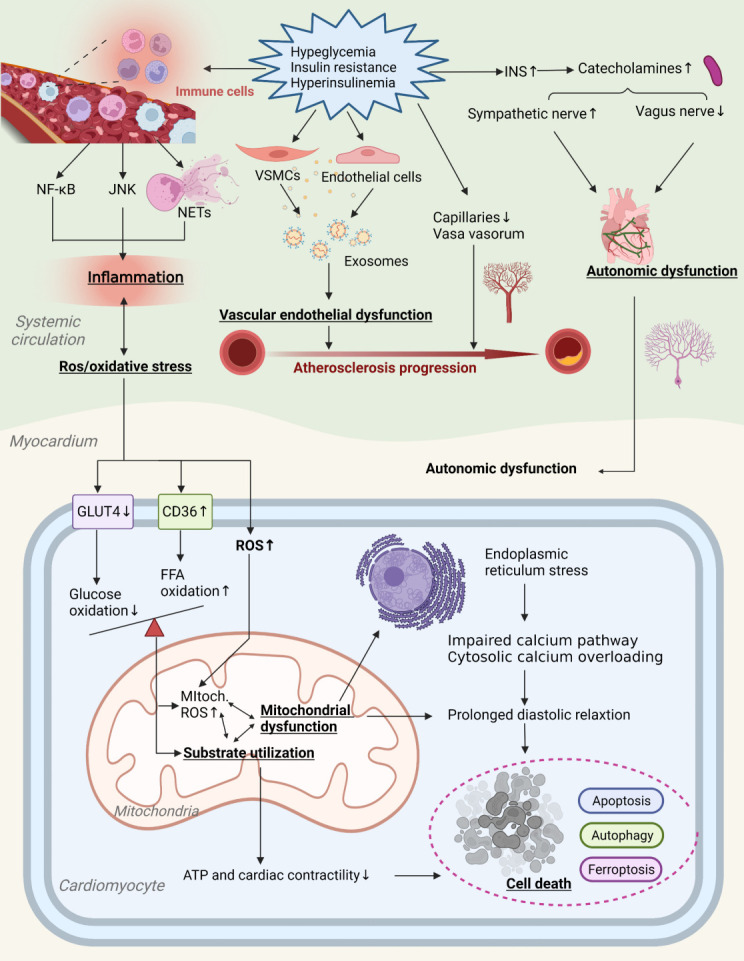
Mechanisms of insulin resistance-induced diabetes heart disease (DHD). Insulin resistance affects the progression of DHD by altering cardiovascular risk factors and reducing the insulin signaling pathway, causing a number of cardiovascular diseases such as myocardial fibrosis, ventricular hypertrophy, atherosclerosis, impaired myocardial systolic and diastolic function, and hypertension. INS, insulinase-like proteases; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; NET, neutrophil extracellular trap; VSMC, vascular smooth muscle cells; GLUT-4, glucose transporter-4; CD36, cluster differentiation protein 36; FFA, free fatty acid; ROS, reactive oxygen species; ATP, adenosine triphosphate.
