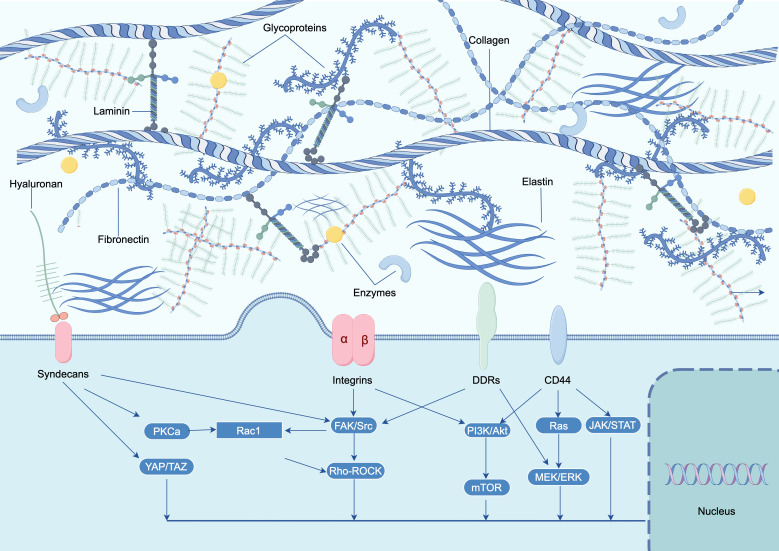
Figure 1.
The modulation of intracellular signaling in TME through alterations of the ECM. The ECM changes play a significant role in influencing various intracellular signaling pathways. The primary mediators of extracellular cues are integrins, which integrate biochemical and biomechanical cues with growth factor signaling and other inputs. Additionally, receptors such as epithelial DDRs, syndecans, and the hyaluronan receptor CD44 transduce matrix signals. Ultimately, these signals regulate multiple cellular functions, including cellular adhesion, cytoskeletal dynamics, cell proliferation, cell survival and differentiation. ECM, extracellular matrix; TME, tumor micro environment; FAK, focal adhesion kinase; GAG, glycosaminoglycan; ROCK, Rho-associated protein kinase; YAP/TAZ, yes-associated protein/transcriptional co-activator with PDZ-binding motif.