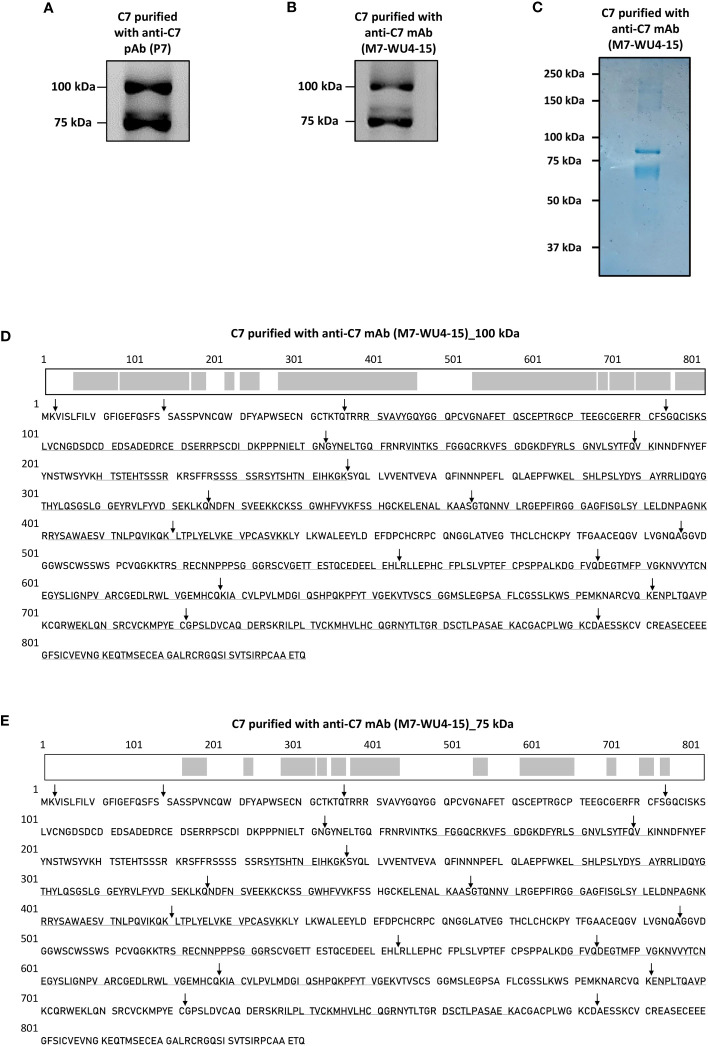
Figure 2.
Detection of a variant form of C7 and screening of C7 aa residues in the visualized variant. (A) C7 purified from NHS-MUI with the anti-C7 pAb, P7, was separated by SDS-PAGE under non-reducing conditions and immunoblot was probed with the anti-C7 mAb, M7-WU4-15. (B) C7 purified from NHS-MUI with M7-WU4-15 was separated by SDS-PAGE under non-reducing conditions and immunoblot was probed with M7-WU4-15. (C) Coomassie staining of C7 purified from NHS-MUI with the anti-C7 mAb, M7-WU4-15, and separated by SDS-PAGE gel under non-reducing conditions. (D) The C7 aa residues identified by LC-MS in the 100 kDa band (1B) are in bold and underlined, along with an illustration of the screened residues in the C7 polypeptide chain highlighted in grey. The screened aa residues are 76% of the total C7 polypeptide chain. (E) The C7 aa residues detected in the 75 kDa band (1B) are in bold and underlined, along with an illustration of the screened residues in the C7 polypeptide chain highlighted in grey. The screened aa residues are 37% of the total C7 polypeptide chain. Black arrows indicate the exon/intron boundaries. Western blots and coomassie staining are representative of at least three independent experiments. Images were taken using the ImageQuant™ LAS 400 camera system.