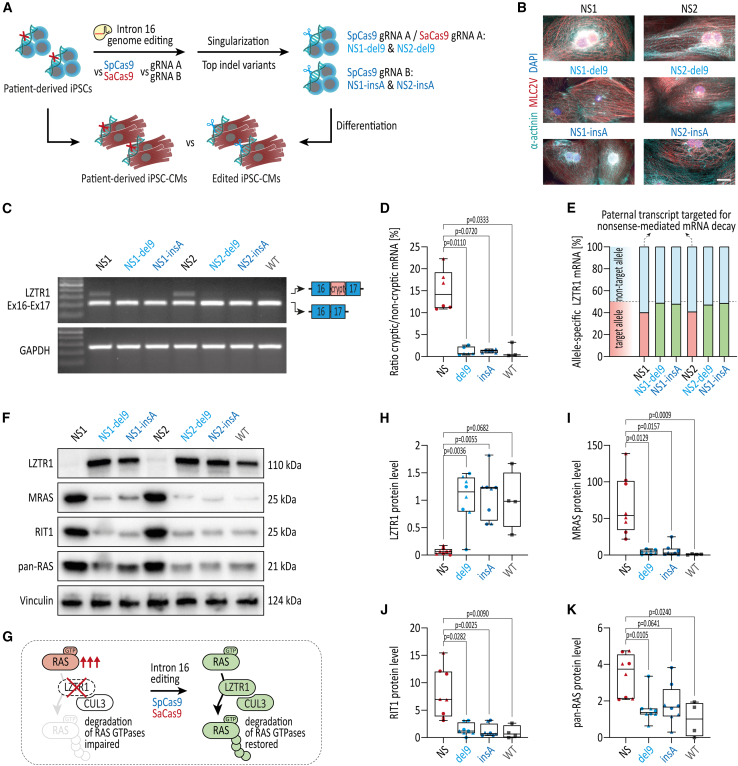
Figure 2.
Restoration of LZTR1 function and normalization of RAS GTPase levels upon CRISPR-Cas9 editing of LZTR1 intron 16 in patient-specific iPSCs
(A) CRISPR-edited iPSCs and unedited patient-specific iPSCs were differentiated into ventricular iPSC-CMs and analyzed for LZTR1 restoration and accumulation of RAS levels as indicator of LZTR1 function at day 30 of differentiation. (B) Representative images of iPSC-CMs stained for α-actinin and ventricular-specific MLC2V indicated a regular and well-organized sarcomeric assembly across all iPSC lines; scale bar, 20 μm. (C) Evaluation of regular splicing of the LZTR1 transcript, assessed by reverse-transcriptase PCR, revealed exclusion of the cryptic exon between exons 16 and 17 in CRISPR-edited iPSC-CMs in comparison with unedited iPSC-CMs from the patients. Analysis of GAPDH expression served as control. (D) Quantification of ratios for abundance of the cryptic exon vs. the non-cryptic variant revealed significant reduction of the cryptic variant in CRISPR-edited iPSC lines; n = 3 individual differentiations per iPSC line. (E) Evaluation of maternal and paternal mRNA transcript expression, assessed by amplicon sequencing, showed escape of the paternal transcript from nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in CRISPR-corrected iPSC-CMs compared with patient-specific iPSC-CMs at day 30 of differentiation. (F) Representative blots of LZTR1, MRAS, RIT1, and pan-RAS (recognizing HRAS, KRAS, and NRAS), assessed by western blot, revealed normalization of RAS GTPase levels in CRISPR-edited iPSC-CMs in comparison with unedited iPSC-CMs from the patients; Vinculin served as loading control. (G) Model of LZTR1-mediated regulation of RAS-MAPK signaling: LZTR1 deficiency causes accumulation of RAS GTPases and hyperactivity of the signaling pathway; CRISPR-Cas9-based gene therapy targeting LZTR1 intron 16 restores LZTR1 function, thereby normalizing RAS-MAPK signaling. (H–K) Quantitative analysis of western blots for LZTR1 (H), MRAS (I), RIT1 (J), and pan-RAS (K); data were normalized to total protein and to the corresponding WT samples on each membrane; n = 4 independent differentiations per iPSC line. Data were analyzed by nonparametric Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s correction and are presented as mean ± SEM (D, H, I, J, K).