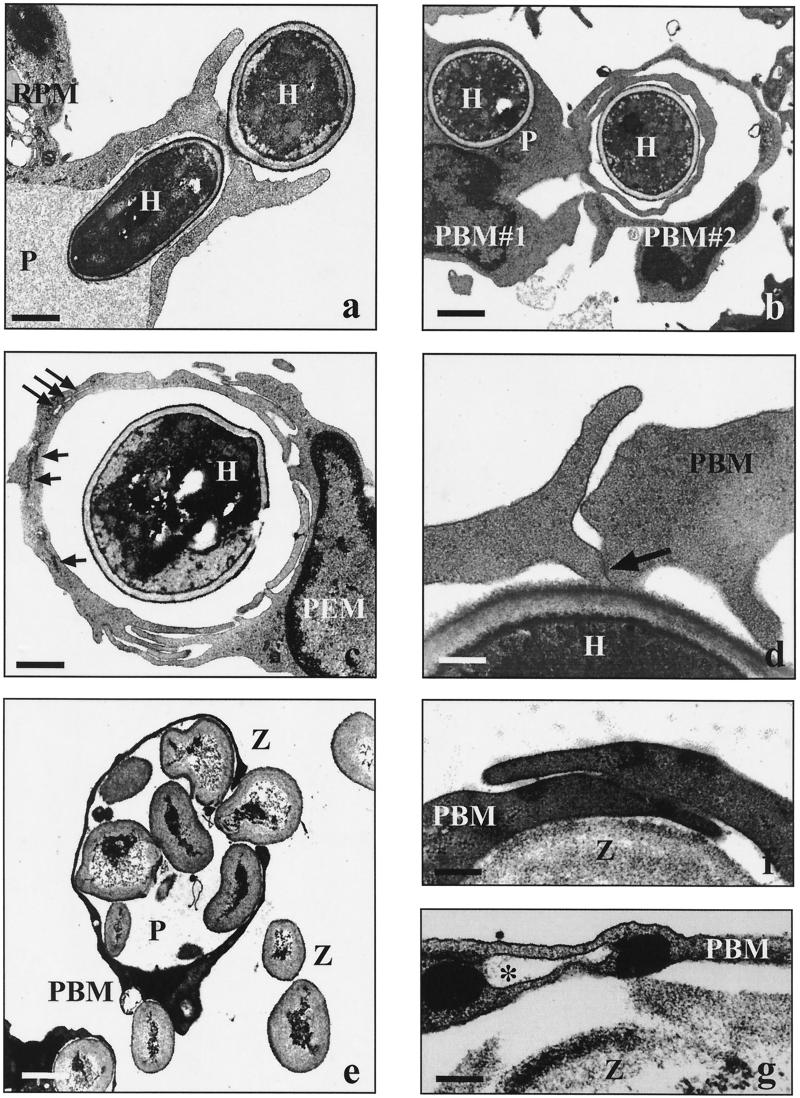
FIG. 6.
Electron micrographs showing the uptake of C. albicans and zymosan particles by human and murine phagocytes. Human peripheral blood monocytes (PBM) and murine resident (RPM) or thioglycolate-elicited (PEM) peritoneal macrophages (2 × 106 each) were incubated with live C. albicans hyphae (H) or zymosan particles (Z) (2 × 107) in the presence of fFCS for incubation periods of 20 min to 8 h unless otherwise indicated. (a) Phagocytosis of C. albicans via a symmetrical phagocytic cup (30 min; P, phagosome; bar = 1.7 μm). (b) Two phagocytes (PBM#1 and PBM#2) simultaneously engulfing C. albicans via overlapping pseudopods (60 min; P, conventional phagosome; bar = 3.0 μm). (c) Various stages of fusion events along the overlapping pseudopods enclosing a heat-killed C. albicans cell (240 min; long arrows, remaining membrane fissures; short arrows, closed membrane fissures; bar = 4.0 μm). (d) Slightly overlapping pseudopods of a PBM in the presence of 1 μg of LPS per ml (30 min; arrow, starting membrane fusion; bar = 0.2 μm). (e) Giant phagosome (P) filled with several zymosan particles (20 min; bar = 2.5 μm). (f) Overlapping pseudopods along a zymosan particle in the absence of serum (20 min; bar = 0.5 μm). (g) Remaining membrane-bounded fissure (asterisk) in the phagosome wall enclosing a zymosan particle, indicative of incomplete fusion of overlapping pseudopods (20 min; bar = 0.1 μm).